Early developmental trajectories of the impaired hand in infants with unilateral cerebral palsy
- PMID: 39826100
- PMCID: PMC12134435
- DOI: 10.1111/dmcn.16240
Early developmental trajectories of the impaired hand in infants with unilateral cerebral palsy
Abstract
Aim: To identify developmental trajectories of impaired hand function in infants aged 3 to 15 months with unilateral cerebral palsy (CP).
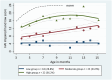
Method: Sixty-three infants (37 male; median gestational age 37 weeks [interquartile range 30-39.1 weeks]) recruited as part of a randomized trial with a confirmed diagnosis of unilateral CP were included. All infants received early upper limb therapy. The Hand Assessment for Infants (HAI) was completed at baseline and until 12 to 15 months corrected age. Group-based trajectory modelling identified groups with similar trajectories of development of impaired hand function. Multinomial logistic regression determined associations between demographic variables and trajectory membership.
Results: The three-group trajectory model comprised 'low' 29%, 'moderate' 35%, and 'high' 36% functioning groups. The relative risk ratio of being in the low or moderate relative to high group increased by 16% (95% confidence interval [CI] 1.02-1.32) and 14% (95% CI 1.01-1.29) respectively for each 1 week increase in gestational age. Males were more likely to be in the low relative to high group (relative risk ratio 7.22; 95% CI 1.6-32.5).
Interpretation: Three distinct trajectories of development of the impaired hand were identified. Males and infants born closer to term age were at higher risk of being in a low group with little improvement over time, despite receiving early intervention.
© 2025 The Author(s). Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Mac Keith Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic corticosteroid regimens for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 13;3(3):CD010941. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010941.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36912887 Free PMC article.
-
Early developmental intervention programmes post-hospital discharge to prevent motor and cognitive impairments in preterm infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12:CD005495. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005495.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 24;(11):CD005495. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005495.pub4. PMID: 23235624 Updated.
-
Intermittent auscultation (IA) of fetal heart rate in labour for fetal well-being.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 13;2(2):CD008680. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008680.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28191626 Free PMC article.
-
Different corticosteroids and regimens for accelerating fetal lung maturation for babies at risk of preterm birth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 9;8(8):CD006764. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006764.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35943347 Free PMC article.
-
Treadmill interventions with partial body weight support in children under six years of age at risk of neuromotor delay.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 7;(12):CD009242. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009242.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 29;7:CD009242. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009242.pub3. PMID: 22161449 Updated.
Cited by
-
Barriers, Facilitators, and a Proposed Model of Care for Implementation of Upper Limb Distributed Practice Approaches for Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 30;14(3):924. doi: 10.3390/jcm14030924. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39941595 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

