Early attainment of 20-hydroxyecdysone threshold shapes mosquito sexual dimorphism in developmental timing
- PMID: 39827175
- PMCID: PMC11743200
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56224-y
Early attainment of 20-hydroxyecdysone threshold shapes mosquito sexual dimorphism in developmental timing
Abstract
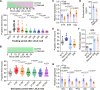
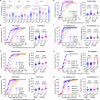
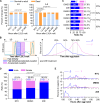
In holometabolous insects, critical weight (CW) attainment triggers pupation and metamorphosis, but its mechanism remains unclear in non-model organisms like mosquitoes. Here, we investigate the role of 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) in CW assessment and pupation timing in Aedes albopictus and Ae. aegypti, vectors of arboviruses including dengue and Zika. Our results show that the attainment of CW is contingent upon surpassing a critical 20E threshold, which results in entrance into a constant 22 h interval and the subsequent 20E pulse responsible for larval-pupal ecdysis. Sexual dimorphism in pupation time arises from higher basal 20E levels in males, enabling earlier CW attainment. Administering 20E at 50% of L3/L4 molt, when most of males but not females pass the pulse, results in female-specific lethality. These findings highlight the pivotal role of 20E thresholds in CW, pupation timing, and sexual dimorphism, suggesting that manipulating 20E levels can skew populations male, offering a potential mosquito sex separation strategy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Z.X. is a co-founder and shareholder of Guangzhou Wolbaki Biotech Co., Ltd and a member of its scientific advisory board. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
AaHR78 mediates the effects of 20E on growth and reproduction in Aedes aegypti.J Insect Physiol. 2025 Apr;162:104790. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2025.104790. Epub 2025 Feb 27. J Insect Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40023247
-
20-Hydroxyecdysone stimulation of juvenile hormone biosynthesis by the mosquito corpora allata.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Sep;64:100-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26255691 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the roles of FTZ-F1 in larval molting and pupation, and the sublethal effects of methoxyfenozide on Helicoverpa armigera.Pest Manag Sci. 2021 Mar;77(3):1328-1338. doi: 10.1002/ps.6146. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Pest Manag Sci. 2021. PMID: 33078511
-
Leptinotarsa hormone receptor 4 (HR4) tunes ecdysteroidogenesis and mediates 20-hydroxyecdysone signaling during larval-pupal metamorphosis.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Mar;94:50-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2017.09.012. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 28951206
-
Ecdysone and the cell cycle: investigations in a mosquito cell line.J Insect Physiol. 2010 Oct;56(10):1396-401. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2010.03.016. Epub 2010 Mar 28. J Insect Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20303973 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Danielsen, E. T., Moeller, M. E. & Rewitz, K. F. Nutrient signaling and developmental timing of maturation. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol.105, 37–67 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Buhler, K. et al. Growth control through regulation of insulin signalling by nutrition-activated steroid hormone in Drosophila. Development145, dev165654 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

