TCTEX1D2 is essential for sperm flagellum formation in mice
- PMID: 39827215
- PMCID: PMC11743150
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-83424-1
TCTEX1D2 is essential for sperm flagellum formation in mice
Abstract
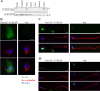
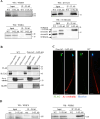
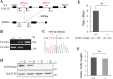
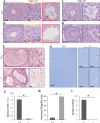
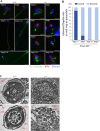
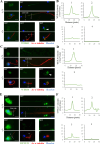
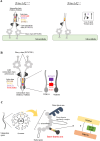
Flagella and cilia are widely conserved motile structures, in mammalian, sperm possess flagella. Large protein complexes called dynein, including cytoplasmic dynein 2 and axonemal dynein, play a role in the formation of cilia and flagella. The function of each subunit component of dynein complexes in sperm flagellum formation remains unclear. One such subunit is TCTEX1D2. Co-immunoprecipitation studies showed that TCTEX1D2 interacted with cytoplasmic dynein 2 subunits WDR34, WDR60, and DYNLT1 in the testes. Furthermore, TCTEX1D2 also interacted with WDR63 and WDR78, subunits of inner dynein arm, which is axonemal dynein. Tctex1d2-/- mice generated in this study exhibited male infertility due to flagellar dysplasia, and the axonemal structures were disrupted inside the flagella. Further, the localization of cytoplasmic dynein 2 subunits was abnormal in in Tctex1d2-/- mice. In contrast, the motile cilia of Tctex1d2-/- mice were normal. Overall, we revealed that TCTEX1D2 is important for the assembly of cytoplasmic dynein 2 and inner dynein arm and functions in two distinct dynein complexes during mouse sperm flagellum formation. This is only in sperm flagellum formation, not in cilia formation.
Keywords: Cytoplasmic dynein 2; Inner dynein arm; Male infertility; Sperm flagella; Spermatogenesis; TCTEX1D2.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Defects in the cytoplasmic assembly of axonemal dynein arms cause morphological abnormalities and dysmotility in sperm cells leading to male infertility.PLoS Genet. 2021 Feb 26;17(2):e1009306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009306. eCollection 2021 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33635866 Free PMC article.
-
Wampa is a dynein subunit required for axonemal assembly and male fertility in Drosophila.Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 15;463(2):158-168. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.04.006. Epub 2020 May 6. Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32387369 Free PMC article.
-
TTC12 Loss-of-Function Mutations Cause Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia and Unveil Distinct Dynein Assembly Mechanisms in Motile Cilia Versus Flagella.Am J Hum Genet. 2020 Feb 6;106(2):153-169. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.12.010. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Am J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 31978331 Free PMC article.
-
Intraflagellar Transport (IFT) and Sperm Formation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1469:395-409. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-82990-1_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40301266 Review.
-
Functional anatomy of the mammalian sperm flagellum.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2016 Nov;73(11):652-669. doi: 10.1002/cm.21338. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2016. PMID: 27712041 Review.
References
-
- Lindemann, C. B. & Lesich, K. A. Functional anatomy of the mammalian sperm flagellum. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken)73, 652–669. 10.1002/cm.21338 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Satir, P. & Christensen, S. T. Overview of structure and function of mammalian cilia. Annu Rev Physiol69, 377–400. 10.1146/annurev.physiol.69.040705.141236 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

