Effects of water-soluble vitamins on glycemic control and insulin resistance in adult type 2 diabetes: an umbrella review of meta-analyses
- PMID: 39828265
- PMCID: PMC11742600
- DOI: 10.6133/apjcn.202502_34(1).0012
Effects of water-soluble vitamins on glycemic control and insulin resistance in adult type 2 diabetes: an umbrella review of meta-analyses
Abstract
Background and objectives: Growing evidence has explored the effects of water-soluble vitamins supplementation on glycemic control and insulin resistance in diabetic patients; however, the results of previous meta-analyses are inconsistent. To address this, we conducted an umbrella review to synthesize the evidence on these effects.
Methods and study design: A systematic literature search in Web of science, PubMed, and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews was performed from 2012 to November 2022. he quality of the meta-analyses was assessed using AMSTAR-2 and GRADE.
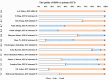
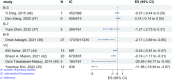
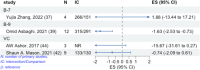
Results: Fourteen systematic reviews and meta-analyses met the inclusion criteria, examining the effects of five water-soluble vitamins (B-1, B-3, biotin, B-9, and C) on glycemic control and insulin resistance. The findings suggest that vitamin C supplementation can improve glycemic control in type 2 diabetes, as indicated by reduced FBG and HbA1c, with more significant effects observed for durations longer than 30 days.
Conclusions: Insulin resistance is improved by folic acid supplementations. More well-designed individual randomized controlled trials are needed in the future, as well as meta-analysis of higher quality.
Keywords: glycemic control; insulin resistance; type 2 diabetes; umbrella review; water-soluble vitamin.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with a financial or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials dis-cussed in this manuscript
Figures




Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Nutrient Supplements for Glycaemic Control and Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: An Umbrella Review and Hierarchical Evidence Synthesis.Nutrients. 2022 May 30;14(11):2295. doi: 10.3390/nu14112295. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35684094 Free PMC article.
-
Folic Acid Supplementation Improves Glycemic Control for Diabetes Prevention and Management: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Nutrients. 2021 Jul 9;13(7):2355. doi: 10.3390/nu13072355. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34371867 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of soluble fiber supplementation on glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Clin Nutr. 2021 Apr;40(4):1800-1810. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.10.032. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Clin Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33162192
-
Folic Acid as a Potential Vitamin in Glycemic Control: A Systematic Review.Curr Nutr Rep. 2024 Dec;13(4):729-750. doi: 10.1007/s13668-024-00565-5. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Curr Nutr Rep. 2024. PMID: 39251542
References
-
- Magliano DJ, Boyko EJ, IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th edition scientific committee . 10th ed. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation; 2021. IDF DIABETES ATLAS [Internet] [cited 2023 Jun 27]. (IDF Diabetes Atlas); Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK581934/ - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

