Synergistic Adhesion and Shape Deformation in Nanowire-Structured Liquid Crystal Elastomers
- PMID: 39828612
- PMCID: PMC11881676
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.202414695
Synergistic Adhesion and Shape Deformation in Nanowire-Structured Liquid Crystal Elastomers
Abstract
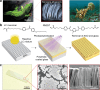
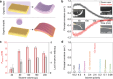
Nature provides many examples of the benefits of nanoscopic surface structures in areas of adhesion and antifouling. Herein, the design, fabrication, and characterization of liquid crystal elastomer (LCE) films are presented with nanowire surface structures that exhibit tunable stimuli-responsive deformations and enhanced adhesion properties. The LCE films are shown to curl toward the side with the nanowires when stimulated by heat or organic solvent vapors. In contrast, when a droplet of the same solvent is placed on the film, it curls away from the nanowire side due to nanowire-induced capillary forces that cause unequal swelling. This characteristic curling deformation is shown to be reversible and can be optimized to match curved substrates, maximizing adhesive shear forces. By using chemical modification, the LCE nanowire films can be given underwater superoleophobicity, enabling oil repellency under a range of harsh conditions. This is combined with the nanowire-induced frictional asymmetry and the reversible shape deformation to create an underwater droplet mixing robot, capable of performing chemical reactions in aqueous environments. These findings demonstrate the potential of nanowire-augmented LCE films for advanced applications in soft robotics, adaptive adhesion, and easy chemical modification, with implications for designing responsive materials that integrate mechanical flexibility with surface functionality.
Keywords: adhesion; liquid crystal elastomers; nanowire structures; stimuli‐responsive materials; superwettability.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Materials published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reversible Curvature Reversal of Monolithic Liquid Crystal Elastomer Film and Its Smart Valve Application.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2021 Nov;42(21):e2100404. doi: 10.1002/marc.202100404. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2021. PMID: 34418205
-
Thermal Gradient-Driven Heterogeneous Actuation of Liquid Crystal Elastomers for a Crawling Robot.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Feb 12;17(6):9992-10003. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c00638. Epub 2025 Jan 30. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 39885638
-
Preparation of Monodomain Liquid Crystal Elastomers and Liquid Crystal Elastomer Nanocomposites.J Vis Exp. 2016 Feb 6;(108):e53688. doi: 10.3791/53688. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 26889665 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-induced Intelligence of Liquid Crystal Elastomers.Chemistry. 2023 Jul 6;29(38):e202301027. doi: 10.1002/chem.202301027. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Chemistry. 2023. PMID: 37129950 Review.
-
Liquid Crystal Elastomers for Biological Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Mar 22;11(3):813. doi: 10.3390/nano11030813. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33810173 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- a) Stuart‐Fox D., Ng L., Elgar M. A., Hölttä‐Otto K., Schröder‐Turk G., Voelcker N. H., Watson G. S., Nat. Rev. Mater. 2023, 8, 565;
- b) Ganewatta M. S., Wang Z. K., Tang C. B., Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 753; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Chen H. W., Zhang P. F., Zhang L. W., Iu H. L. L., Jiang Y., Zhang D. Y., Han Z. W., Jiang L., Nature 2016, 532, 85; - PubMed
- d) Wong T. S., Kang S. H., Tang S. K. Y., Smythe E. J., Hatton B. D., Grinthal A., Aizenberg J., Nature 2011, 477, 443. - PubMed
-
- a) Chen W., Zhang P., Yu S., Zang R., Xu L., Wang S., Wang B., Meng J., Nat. Protoc. 2022, 17, 2647; - PubMed
- b) Liu M. J., Wang S. T., Wei Z. X., Song Y. L., Jiang L., Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 665.
-
- a) Li Z. H., Guo Z. G., Nanoscale 2019, 11, 22636; - PubMed
- b) Babi A., Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17035;
- c) Liu M. J., Wang S. T., Jiang L., Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17036.
-
- a) Jo W., Kang H. S., Choi J., Jung J., Hyun J., Kwon J., Kim I., Lee H., Kim H. T., Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 5500; - PubMed
- b) Ball P., Nature 1999, 400, 507.
-
- a) Maderson P. F. A., Nature 1964, 203, 780;
- b) Autumn K., Liang Y. A., Hsieh S. T., Zesch W., Chan W. P., Kenny T. W., Fearing R., Full R. J., Nature 2000, 405, 681; - PubMed
- c) Lee H., Lee B. P., Messersmith P. B., Nature 2007, 448, 338; - PubMed
- d) Qu L. T., Dai L. M., Stone M., Xia Z. H., Wang Z. L., Science 2008, 322, 238; - PubMed
- e) Cai Y., Lin L., Xue Z., Liu M., Wang S., Jiang L., Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 24, 809;
- f) Johnson K. L., Kendall K., Roberts A. D., Proc. R. Soc. London A. 1971, 324, 301.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

