Green Synthesis of Tetrahydropyrazino[2,1-a:5,4-a']diisoquinolines as SARS-CoV-2 Entry Inhibitors
- PMID: 39829498
- PMCID: PMC11740144
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c08640
Green Synthesis of Tetrahydropyrazino[2,1-a:5,4-a']diisoquinolines as SARS-CoV-2 Entry Inhibitors
Abstract
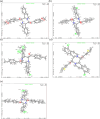
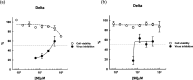
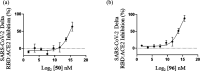
A class of tetrahydropyrazino[2,1-a:5,4-a']diisoquinoline derivatives were synthesized under environmentally friendly conditions using water as the solvent. The 3-D structures of some synthesized compounds were determined by X-ray diffraction. Since naturally occurring isoquinoline alkaloids have significant antiviral activities against a wide range of viruses, including coronaviruses, the synthesized compounds were assayed for their inhibitory activities against SARS-CoV-2. Our results showed that the active compounds 50 and 96 blocked the delta SARS-CoV-2 entry into VeroE6 cells to display EC50 of 26.5 ± 6.9 and 17.0 ± 3.7 μM, respectively, by inhibiting the interaction between SARS-CoV-2 Spike's receptor binding domain (RBD) and human receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), and CC50 greater than 100 μM. This study provides a green synthesis method of tetrahydropyrazinodiisoquinoline for antiviral or other applications.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synthesis, evaluation, and mechanism of 1-(4-(arylethylenylcarbonyl)phenyl)-4-carboxy-2-pyrrolidinones as potent reversible SARS-CoV-2 entry inhibitors.Antiviral Res. 2023 Nov;219:105735. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2023.105735. Epub 2023 Oct 18. Antiviral Res. 2023. PMID: 37858764
-
The use of Pseudotyped Coronaviruses for the Screening of Entry Inhibitors: Green Tea Extract Inhibits the Entry of SARS-CoV-1, MERSCoV, and SARS-CoV-2 by Blocking Receptor-spike Interaction.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022;23(8):1118-1129. doi: 10.2174/1389201022666210810111716. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34375189
-
Multidisciplinary Approaches Identify Compounds that Bind to Human ACE2 or SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein as Candidates to Block SARS-CoV-2-ACE2 Receptor Interactions.mBio. 2021 Mar 30;12(2):e03681-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03681-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33785634 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of S-protein RBD and hACE2 Interaction for Control of SARSCoV- 2 Infection (COVID-19).Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(6):689-703. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666201117111259. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33208074 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of green tea catechin, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCG) in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Major interactions with host/virus proteases.Phytomed Plus. 2023 Feb;3(1):100402. doi: 10.1016/j.phyplu.2022.100402. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Phytomed Plus. 2023. PMID: 36597465 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huang C.; Wang Y.; Li X.; Ren L.; Zhao J.; Hu Y.; Zhang L.; Fan G.; Xu J.; Gu X.; Cheng Z.; Yu T.; Xia J.; Wei Y.; Wu W.; Xie X.; Yin W.; Li H.; Liu M.; Xiao Y.; Gao H.; Guo L.; Xie J.; Wang G.; Jiang R.; Gao Z.; Jin Q.; Wang J.; Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395 (10223), 497–506. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu F.; Zhao S.; Yu B.; Chen Y. M.; Wang W.; Song Z. G.; Hu Y.; Tao Z. W.; Tian J. H.; Pei Y. Y.; Yuan M. L.; Zhang Y. L.; Dai F. H.; Liu Y.; Wang Q. M.; Zheng J. J.; Xu L.; Holmes E. C.; Zhang Y. Z. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579 (7798), 265–269. 10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu N.; Zhang D.; Wang W.; Li X.; Yang B.; Song J.; Zhao X.; Huang B.; Shi W.; Lu R.; Niu P.; Zhan F.; Ma X.; Wang D.; Xu W.; Wu G.; Gao G. F.; Tan W. China novel coronavirus investigating and research team. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382 (8), 727–733. 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou P.; Yang X. L.; Wang X. G.; Hu B.; Zhang L.; Zhang W.; Si H. R.; Zhu Y.; Li B.; Huang C. L.; Chen H. D.; Chen J.; Luo Y.; Guo H.; Jiang R. D.; Liu M. Q.; Chen Y.; Shen X. R.; Wang X.; Zheng X. S.; Zhao K.; Chen Q. J.; Deng F.; Liu L. L.; Yan B.; Zhan F. X.; Wang Y. Y.; Xiao G. F.; Shi Z. L. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu R.; Zhao X.; Li J.; Niu P.; Yang B.; Wu H.; Wang W.; Song H.; Huang B.; Zhu N.; Bi Y.; Ma X.; Zhan F.; Wang L.; Hu T.; Zhou H.; Hu Z.; Zhou W.; Zhao L.; Chen J.; Meng Y.; Wang J.; Lin Y.; Yuan J.; Xie Z.; Ma J.; Liu W. J.; Wang D.; Xu W.; Holmes E. C.; Gao G. F.; Wu G.; Chen W.; Shi W.; Tan W. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395 (10224), 565–574. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
