This is a preprint.
Metabolic tagging reveals surface-associated lipoproteins in mycobacteria
- PMID: 39829771
- PMCID: PMC11741404
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.01.07.631728
Metabolic tagging reveals surface-associated lipoproteins in mycobacteria
Update in
-
Metabolic Tagging Reveals Surface-Associated Lipoproteins in Mycobacteria.ACS Infect Dis. 2025 Oct 10;11(10):2754-2765. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.5c00365. Epub 2025 Sep 12. ACS Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40940670
Abstract
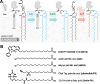
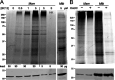
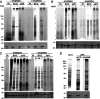
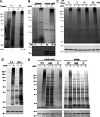
Mycobacteria such as the causative agent of tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, encode over 100 bioinformatically predicted lipoproteins. Despite the importance of these posttranslationally modified proteins for mycobacterial survival, many remain experimentally unconfirmed. Here we characterized metabolic incorporation of diverse fatty acid analogues as a facile method of adding chemical groups that enable downstream applications such as detection, crosslinking and enrichment, of not only lipid-modified proteins, but also their protein interactors. Having shown that incorporation is an active process dependent on the lipoprotein biosynthesis pathway, we discovered that lipid-modified proteins are also located at the mycobacterial cell surface even though mycobacteria do not encode known lipoprotein transporters. These data have implications for uncovering a novel transport pathway and the roles of lipoproteins at the interface with the host environment. Our findings and the tools we developed will enable the further study of pathways related to lipoprotein function and metabolism in mycobacteria and other bacteria in which lipoproteins remain poorly understood.
Keywords: fatty acids; lipoproteins; mycobacteria; surface proteins.
Figures


References
-
- McGowen K.; Funck T.; Wang X.; Zinga S.; Wolf I. D.; Akusobi C.; Denkinger C. M.; Rubin E. J.; Sullivan M. R. Efflux Pumps and Membrane Permeability Contribute to Intrinsic Antibiotic Resistance in Mycobacterium Abscessus. PLOS Pathogens 2025, 21 (4), e1013027. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dash R.; Liu Z.; Lepori I.; Chordia M. D.; Ocius K.; Holsinger K.; Zhang H.; Kenyon R.; Im W.; Siegrist M. S.; Pires M. M. Systematic Determination of the Impact of Structural Edits on Peptide Accumulation into Mycobacteria. bioRxiv 2025, 2025.01.17.633618. 10.1101/2025.01.17.633618. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
