Association between chronic kidney disease and oxidative balance score: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2005-2018
- PMID: 39830066
- PMCID: PMC11738952
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1406780
Association between chronic kidney disease and oxidative balance score: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2005-2018
Abstract
Background: The oxidative balance score (OBS) is a comprehensive concept that includes 16 dietary components and four lifestyle factors to assess an individual's exposure to pro-oxidants and antioxidants. This study aims to explore the relationship between OBS and the risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
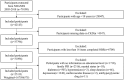
Methods: This cross-sectional study included nationally representative National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) participants aged 18 and above from 2005 to 2018. The OBS, a novel concept derived from multiple dietary (pro-oxidant and antioxidant nutrients) and lifestyle exposures (including smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, and physical activity), serves as a useful tool for assessing an individual's oxidative stress status. The continuous variable OBS was converted into categorical variables by quartiles. Covariates included age, gender, race, education level, marital status, poverty-income ratio, sleep duration, depression, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular disease, use of hypoglycemic medications, and use of antihypertensive medications. The relationship between OBS and CKD was explored using multiple logistic regression analysis and restricted cubic spline models. Additionally, subgroup analyses, interaction tests, and sensitivity analyses were conducted to validate the stability of the results.
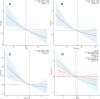
Results: A total of 25,118 NHANES participants were included in this study. The weighted prevalence of CKD was 14.97%. In the fully adjusted model, compared to the lowest OBS quartile, participants in the highest quartile had a 26% reduced risk of CKD (OR = 0.74, 95%CI: 0.63-0.87, p < 0.001). In restricted cubic spline regression, there was a linear association between OBS and CKD. The results of subgroup analysis and sensitivity analysis remain consistent. A significant interaction was found in the stratified analysis by age group (p for interaction = 0.012), suggesting that individuals older than 60 years may benefit more significantly from an increase in OBS scores compared to those aged 60 years or younger.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that higher OBS is associated with a lower risk of CKD, particularly among the elderly population, providing innovative insights and preliminary evidence for the development of preventive strategies against CKD.
Keywords: NHANES; a cross-sectional study; chronic kidney disease; dietary components; oxidative balance score.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Yang, Li, Deng, He, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources