Environment signal dependent biocontainment systems for engineered organisms: Leveraging triggered responses and combinatorial systems
- PMID: 39830078
- PMCID: PMC11741035
- DOI: 10.1016/j.synbio.2024.12.005
Environment signal dependent biocontainment systems for engineered organisms: Leveraging triggered responses and combinatorial systems
Abstract
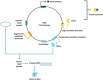
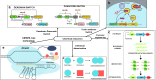
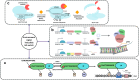
As synthetic biology advances, the necessity for robust biocontainment strategies for genetically engineered organisms (GEOs) grows increasingly critical to mitigate biosafety risks related to their potential environmental release. This paper aims to evaluate environment signal-dependent biocontainment systems for engineered organisms, focusing specifically on leveraging triggered responses and combinatorial systems. There are different types of triggers-chemical, light, temperature, and pH-this review illustrates how these systems can be designed to respond to environmental signals, ensuring a higher safety profile. It also focuses on combinatorial biocontainment to avoid consequences of unintended GEO release into an external environment. Case studies are discussed to demonstrate the practical applications of these systems in real-world scenarios.
Keywords: Biocontainment; Combinatorial systems; Engineered organisms; Genetic circuits; Kill switches; Synthetic biology; Triggered responses.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Wang F., Zhang W. Synthetic biology: recent progress, biosafety and biosecurity concerns, and possible solutions. J Biosaf Biosecur. 2019;1:22–30. doi: 10.1016/J.JOBB.2018.12.003. - DOI
-
- Pavão G., Sfalcin I., Bonatto D. Biocontainment techniques and applications for yeast biotechnology. Fermentation. 2023;9:341. doi: 10.3390/FERMENTATION9040341. 2023;9:341. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

