In Vitro models of leukemia development: the role of very small leukemic stem-like cells in the cellular transformation cascade
- PMID: 39830209
- PMCID: PMC11740207
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1463807
In Vitro models of leukemia development: the role of very small leukemic stem-like cells in the cellular transformation cascade
Abstract
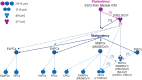
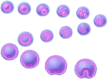
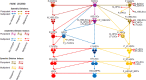
Recent experimental findings indicate that cancer stem cells originate from transformed very small embryonic-like stem cells. This finding represents an essential advancement in uncovering the processes that drive the onset and progression of cancer. In continuously growing cell lines, for the first time, our team's follow-up research on leukemia, lung cancer, and healthy embryonic kidney cells revealed stages that resembles very small precursor stem cells. This review explores the origin of leukemic stem-like cells from very small leukemic stem-like cells establish from transformed very small embryonic-like stem cells. We explore theoretical model of acute myeloid leukemia initiation and progresses through various stages, as well basing the HL60 cell line, present its hierarchical stage development in vitro, highlighting the role of these very small precursor primitive stages. We also discuss the potential implications of further research into these unique cellular stages for advancing leukemia and cancer treatment and prevention.
Keywords: A549; HL60; acute myeloid leukemia development in vitro; cellular transformations; very small leukemic stem-like cells; very small progenitor and precursor stem cells.
Copyright © 2025 Lica, Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka and Hellmann.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Recent progress in leukemic stem cell research for childhood leukemia].Rinsho Ketsueki. 2015 Oct;56(10):1871-81. doi: 10.11406/rinketsu.56.1871. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2015. PMID: 26458424 Japanese.
-
(Very) Small Stem-like Cells in Human Cell Cultures.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 22;15(23):5520. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235520. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067224 Free PMC article.
-
Leukemia stem cells and human acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Semin Hematol. 2009 Jan;46(1):33-8. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2008.09.010. Semin Hematol. 2009. PMID: 19100366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and epigenetic alterations in normal and malignant myelopoiesis in human leukemia 60 (HL60) promyelocytic cell line model.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 2;11:1060537. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1060537. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36819104 Free PMC article.
-
Acute promyelocytic leukemia: where does it stem from?Leukemia. 2004 Mar;18(3):375-84. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2403234. Leukemia. 2004. PMID: 14737069 Review.
References
-
- Aljurf M., Chaudhri N. A., Almhareb F., Walter C. U., Nounou R., Khalil S., et al. (2011). CD34 expression in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a favorable prognostic factor in patients treated with stem cell transplant in first remission. Blood 118, 4091. 10.1182/BLOOD.V118.21.4091.4091 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

