This is a preprint.
Molnupiravir clinical trial simulation suggests that polymerase chain reaction underestimates antiviral potency against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 39830263
- PMCID: PMC11741452
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.11.21.24317726
Molnupiravir clinical trial simulation suggests that polymerase chain reaction underestimates antiviral potency against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
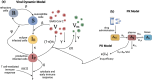
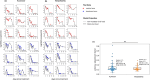
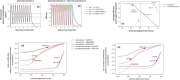
Molnupiravir is an antiviral medicine that induces lethal copying errors during SARS-CoV-2 RNA replication. Molnupiravir reduced hospitalization in one pivotal trial by 50% and had variable effects on reducing viral RNA levels in three separate trials. We used mathematical models to simulate these trials and closely recapitulated their virologic outcomes. Model simulations suggest lower antiviral potency against pre-omicron SARS-CoV-2 variants than against omicron. We estimate that in vitro assays underestimate in vivo potency 7-8 fold against omicron variants. Our model suggests that because polymerase chain reaction detects molnupiravir mutated variants, the true reduction in non-mutated viral RNA is underestimated by ~0.5 log10 in the two trials conducted while omicron variants dominated. Viral area under the curve estimates differ significantly between non-mutated and mutated viral RNA. Our results reinforce past work suggesting that in vitro assays are unreliable for estimating in vivo antiviral drug potency and suggest that virologic endpoints for respiratory virus clinical trials should be catered to the drug mechanism of action.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Combinations of Host- and Virus-Targeting Antiviral Drugs Confer Synergistic Suppression of SARS-CoV-2.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0333122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03331-22. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36190406 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral Efficacy and Safety of Molnupiravir Against Omicron Variant Infection: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 15;13:939573. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.939573. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35784723 Free PMC article.
-
Virologic Outcomes with Molnupiravir in Non-hospitalized Adult Patients with COVID-19 from the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled MOVe-OUT Trial.Infect Dis Ther. 2023 Dec;12(12):2725-2743. doi: 10.1007/s40121-023-00891-1. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Infect Dis Ther. 2023. PMID: 37995070 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral activity of molnupiravir against COVID-19: a schematic review of evidences.Bull Natl Res Cent. 2022;46(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s42269-022-00753-9. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Bull Natl Res Cent. 2022. PMID: 35287311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molnupiravir: an antiviral drug against COVID-19.Arch Virol. 2023 Sep 15;168(10):252. doi: 10.1007/s00705-023-05881-9. Arch Virol. 2023. PMID: 37710056 Review.
References
-
- Jayk Bernal A, Gomes da Silva MM, Musungaie DB, Kovalchuk E, Gonzalez A, Delos Reyes V, Martín-Quirós A, Caraco Y, Williams-Diaz A, Brown ML, Du J, Pedley A, Assaid C, Strizki J, Grobler JA, Shamsuddin HH, Tipping R, Wan H, Paschke A, ..., Group M-OS. Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(6):509–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2116044. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Butler CC, Hobbs FDR, Gbinigie OA, Rahman NM, Hayward G, Richards DB, Dorward J, Lowe DM, Standing JF, Breuer J, Khoo S, Petrou S, Hood K, Nguyen-Van-Tam JS, Patel MG, Saville BR, Marion J, Ogburn E, Allen J, ..., Group PTC. Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2023;401(10373):281–93. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schilling WHK, Jittamala P, Watson JA, Boyd S, Luvira V, Siripoon T, Ngamprasertchai T, Batty EM, Cruz C, Callery JJ, Singh S, Saroj M, Kruabkontho V, Ngernseng T, Tanglakmankhong N, Tubprasert J, Abdad MY, Madmanee W, Kouhathong J, ..., Group PC. Antiviral efficacy of molnupiravir versus ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir in patients with early symptomatic COVID-19 (PLATCOV): an open-label, phase 2, randomised, controlled, adaptive trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024;24(1):36–45. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00493-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, Abreu P, Bao W, Wisemandle W, Baniecki M, Hendrick VM, Damle B, Simón-Campos A, Pypstra R, Rusnak JM, Investigators E-H. Oral Nirmatrelvir for High-Risk, Nonhospitalized Adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(15):1397–408. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2118542. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
