Metabolic response to burn injury: a comprehensive bibliometric study
- PMID: 39830385
- PMCID: PMC11739346
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1451371
Metabolic response to burn injury: a comprehensive bibliometric study
Abstract
Objective: Burns lead to systemic changes manifested by systemic disturbances in water-electrolyte balance and systemic metabolic and inflammatory responses. The hypermetabolic response after a burn injury relies on metabolic, hormonal, and inflammatory dysregulation mechanisms. This study aimed to provide a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of the burn metabolism research field, identifying key trends, influential contributors, and emerging research hotspots to inform future investigative efforts. Ultimately, we conducted an extensive review of the literature, synthesizing the findings to clarify the present understanding within our field of study.
Methods: We obtained 8,823 scientific publications on burn injury and metabolism from the core Web of Science (WOS) database collection. In this work, biblioshiny was used to visualize and analyze the data, and VOSviewer was used to verify the results.
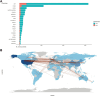
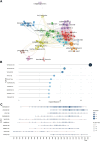
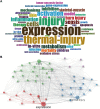
Results: From a total of 8,823 publications, we found a general upward trend in annual publications and citation frequency. According to Bradford's Law, 21 high-production journals were classified as core sources based on the number of publications, and the most productive journal was Burns. The most published countries and authors in this field were the United States and Herndon DN. The most local cited document in this field was the article titled "Catecholamines: Mediator of the Hypermetabolic Response to Thermal Injury" authored by Wilmore DW. The thematic map showed that studies on injury, thermal injury, and sepsis were relatively mature. In contrast, research on metabolism, stress, and responses, and research on mortality, resistance, and management were less well-developed but were essential for the field.
Conclusion: Research on burns and metabolism is increasing. Based on the bibliometric analysis, our study summarized the complex interplay between burn-induced systemic metabolic alterations and inflammatory responses, emphasizing the significance of hypermetabolism and its management. The role of propranolol, insulin, oxandrolone, and nutritional interventions in modulating the hypermetabolic state was discussed. Additionally, our study underscored the challenges of managing sepsis and drug-resistant infections in burn patients as an important future area of research.
Keywords: burn injury; inflammatory; management; metabolism; thermal injury.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Liu, Xie, Zhu, Ding, Zhang, Xian, Wu, Sun, Yan, Lu, Yao, Qian, Lu, Yang, Xu, Huang and Ji.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A bibliometric analysis of publications on burn sepsis using VOSviewer.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 14;9:971393. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.971393. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36186821 Free PMC article.
-
Global Highly Cited Publication Trends and Research Hotspots in Osteoporosis and Bone Metabolic Cells: A Bibliometric and Visualization Analysis from 2013 to 2023.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2025;25(5):386-399. doi: 10.2174/0118715303300989240702043834. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 39005119
-
Bibliometric analysis of laryngeal cancer treatment literature (2003-2023).Heliyon. 2024 Dec 16;11(1):e40832. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40832. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39811326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research hotspots and future trends in lipid metabolism in chronic kidney disease: a bibliometric and visualization analysis from 2004 to 2023.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 3;15:1401939. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1401939. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39290864 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of global literature productivity in systemic lupus erythematosus from 2013 to 2022.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Jan;43(1):175-187. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06728-z. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 37668951
Cited by
-
Disclosing the development and focus of sequencing and omics studies in kidney neoplasm research.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 26;16(1):928. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02750-6. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40418308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schaefer TJ, Tannan SC. Thermal burns. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; (2024). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

