A Case of Eltrombopag-Induced Thrombotic Microangiopathy Initiating Hemodialysis
- PMID: 39830571
- PMCID: PMC11740830
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.75947
A Case of Eltrombopag-Induced Thrombotic Microangiopathy Initiating Hemodialysis
Abstract
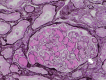
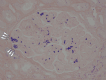
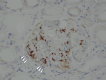
Thrombopoietin receptor agonists are used in addition to steroids for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. A 55-year-old male with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, treated with eltrombopag, developed a rapid decline in renal function following the increase in eltrombopag dose. Renal biopsy showed glomerular endothelial disorder and platelet thrombus, which suggested eltrombopag-induced renal-limited thrombotic microangiopathy. He was treated with steroids; however, his renal function did not improve, and hemodialysis was initiated. During the treatment, acute myocardial infarction and arteriovenous fistula obstruction occurred. After that, he was subsequently diagnosed with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Eltrombopag can cause thrombotic microangiopathy and, in some cases, result in renal failure. Patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura coexisted with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome are at increased risk of thrombosis with thrombopoietin agonists and require careful follow-up.
Keywords: antiphospholipid syndrome; eltrombopag; end-stage renal disease (esrd); idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura; thrombotic microangiopathy.
Copyright © 2024, Fukuda et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Nagasaki Harbor Medical Center Institutional Review Board issued approval not applicable. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Acute Renal Thrombotic Microangiopathy Caused by Eltrombopag and Romiplostim in a Patient with Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) and Underlying Antiphospholipid Syndrome.Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2024 May 31;11(7):004564. doi: 10.12890/2024_004564. eCollection 2024. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 38984183 Free PMC article.
-
Eltrombopag Induced Thrombosis: A Case with Acute Myocardial Infarction.Curr Drug Saf. 2016;11(2):174-6. doi: 10.2174/1574886311207040255. Curr Drug Saf. 2016. PMID: 26560493
-
A Case of Acute Kidney Injury During Eltrombopag Use Successfully Treated With Plasma Exchange in Addition to Antithrombotic Therapy.Kidney Med. 2025 Apr 15;7(6):101007. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2025.101007. eCollection 2025 Jun. Kidney Med. 2025. PMID: 40510611 Free PMC article.
-
Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome in lupus-associated immune thrombocytopenia treated with eltrombopag A case series and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Feb 10;102(6):e32949. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032949. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 36820549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2004:407-23. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2004.1.407. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2004. PMID: 15561695 Review.
References
-
- Tolerability and efficacy of eltrombopag in chronic immune thrombocytopenia: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Elgebaly AS, Ashal GE, Elfil M, Menshawy A. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2017;23:928–937. - PubMed
-
- Thrombopoietin-induced signal transduction and potentiation of platelet activation. Oda A, Miyakawa Y, Druker BJ, et al. Thromb Haemost. 1999;82:377–384. - PubMed
-
- Eltrombopag for management of chronic immune thrombocytopenia (RAISE): a 6-month, randomised, phase 3 study. Cheng G, Saleh MN, Marcher C, et al. Lancet. 2011;377:393–402. - PubMed
-
- International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, et al. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:295–306. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
