The trends of lung cancer burden in BRICS from 1990 to 2021 and its projection to 2035
- PMID: 39830644
- PMCID: PMC11739153
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1511530
The trends of lung cancer burden in BRICS from 1990 to 2021 and its projection to 2035
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer has become the malignant tumor with the highest morbidity and mortality in the world. This study aims to analyze the burden of lung cancer and risk factors associated with lung cancer in the BRICS from 1990-2021 and to project the burden of lung cancer in the BRICS from 2021-2035.
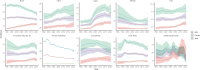
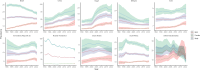
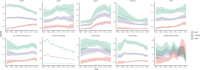
Methods: The Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 database was searched to collect the incidence, prevalence, mortality, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and risk factors of lung cancer in the BRICS. Trends in lung cancer burden from 1990-2021 were analyzed using Joinpoint 4.9.1.0, and Bayesian age-period-cohort (BAPC) analyses were performed using R4.4.1 to project the disease burden of lung cancer from 2021-2035.
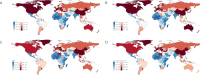
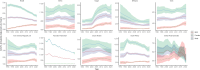
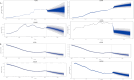
Results: AAPC(average annual percentage change) and EAPC(estimated average percentage change) of ASIR(age-standardized incidence), ASPR(age-standardized prevalence), ASMR(age-standardized mortality), and ASDR(age-standardized disability-adjusted life year) for lung cancer in Brazil, Russia, and Ethiopia 1990-2021 were less than 0. Egypt's AAPC and EAPC for ASIR, ASPR, ASMR, and ASDR were all greater than 0 for 1990-2021, and China's ASIR, ASPR, ASMR, and ASDR were all at the top of the BRICS in 2021. According to BAPC projection Brazil, Iran, Russia, and South Africa will have a decreasing trend in ASIR, ASPR, ASMR, and ASDR from 2021-2035. Egypt will have an increasing trend in ASIR, ASPR, ASMR, and ASDR from 2021-2035. With the exception of Ethiopia, the top tier level 1 and level 2 risk factors in the rest of the BRICS were behavioral factors and smoking factors, respectively.
Conclusion: The BRICS still have a heavy burden of lung cancer, and there are significant differences in the burden of lung cancer among the BRICS. At the same time, many BRICS lung cancer prevention and control measures are worth learning from other developing countries.
Keywords: BRICS; GBD database; burden of disease; lung cancer; risk factors.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Zhu, Wang and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Burden of uterine cancer in China from 1990 to 2021 and 15-year projection: a systematic analysis and comparison with global levels.Reprod Health. 2024 Oct 10;21(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12978-024-01882-2. Reprod Health. 2024. PMID: 39390595 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of trends in the burden of motor neuron disease in China, the United States, and globally from 1990 to 2021: projections for 2022-2041.Front Neurol. 2025 May 16;16:1539889. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1539889. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40452765 Free PMC article.
-
Disparities in the global burden of tracheal, bronchus, and lung cancer from 1990 to 2019.Chin Med J Pulm Crit Care Med. 2023 Mar 28;1(1):36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.pccm.2023.02.001. eCollection 2023 Mar. Chin Med J Pulm Crit Care Med. 2023. PMID: 39170872 Free PMC article.
-
Global burden, risk factors, and projections of early-onset dementia: Insights from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Ageing Res Rev. 2025 Feb;104:102644. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102644. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Ageing Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 39701185 Review.
-
Global and China trends and forecasts of disease burden for female lung Cancer from 1990 to 2021: a study based on the global burden of disease 2021 database.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025 Feb 8;151(2):68. doi: 10.1007/s00432-025-06084-2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39921760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xin HS. (2024). Available online at: https://www.gov.cn/yaowen/liebiao/202405/content_6949027.htm (Accessed September 21, 2024).
-
- Zhang M, Jin W, Tian Y, Zhu H, Zou N, Jia Y, et al. . Cancer burden variations and convergences in globalization: a comparative study on the tracheal, bronchus, and lung (tbl) and liver cancer burdens among who regions from 1990 to 2019. J Epidemiol Glob Health. (2023) 13:696–724. doi: 10.1007/s44197-023-00144-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

