Ellagic Acid Modulates Necroptosis, Autophagy, Inflammations, and Stress to Ameliorate Nonalcoholic Liver Fatty Disease in a Rat Model
- PMID: 39830906
- PMCID: PMC11742184
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.4694
Ellagic Acid Modulates Necroptosis, Autophagy, Inflammations, and Stress to Ameliorate Nonalcoholic Liver Fatty Disease in a Rat Model
Abstract
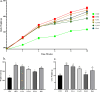
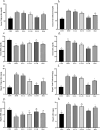
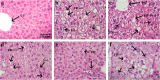
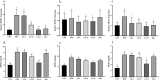
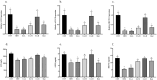
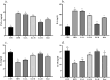
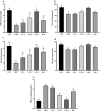
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is considered one of the most common metabolic disorders worldwide. Although the pathoetiology of NAFLD is not fully elucidated, recent evidence suggests the involvement of stress, inflammation, and programmed death in the onset and progression of the disease. This investigation aimed to evaluate the effects of ellagic acid (EA), a known herbal antioxidant, on a high-fat diet (HFD)-induced animal model of NAFLD by evaluating the status of lipid profile, necroptosis (RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL), autophagy (LC3, ATG5, and BECN1), inflammation (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-4, and IL-10), and stress (SOD, CAT, GR, GPx, and MDA). In this regard, rats were randomly divided into 6 groups as follows: normal diet controls, HFD (supplemented with high caloric diet model), EA low dose (HFD and 10 mg/kg/day EA), EA middle dose (HFD and 25 mg/kg/day EA), EA high dose (HFD and 50 mg/kg/day EA), and Rosiglitazone (HFD and 10 mg/kg/day Rosi). After the treatment, the levels of markers related to necroptosis and autophagy in the liver tissue as well as the lipid profiles, inflammation, and oxidative stress status were analyzed. It was shown that the dose of EA was able to improve the weight gain and lipid profile when compared to NAFLD animals (p-value < 0.001). Moreover, EA increased the level of LC3 and ATG5 while decreasing BECN 1, RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL compared to the HFD-induced NAFLD rats (p-value < 0.05). TNF-α and IL-6 were decreased after EA administration, whereas IL-4 and IL-10 levels were increased (p-value < 0.001). Furthermore, the increase in the activity of SOD, CAT, GR, and GPx along with the decrease in MDA levels indicated the suppression of oxidative stress by EA treatment compared to the NAFLD rats (p-value < 0.0001). The current findings may suggest that EA improves NAFLD via modulation of necroptosis, autophagy, inflammation, and stress.
Keywords: NAFLD; autophagy; ellagic acid; metabolism; necroptosis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 improves experimental non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.J Hepatol. 2020 Apr;72(4):627-635. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.11.008. Epub 2019 Nov 21. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31760070
-
Phoenixin 14 Inhibits High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Experimental Mice.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Sep 22;14:3865-3874. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S258857. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 33061293 Free PMC article.
-
Canagliflozin Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Lipid Metabolism and Inhibiting Inflammation through Induction of Autophagy.Yonsei Med J. 2022 Jul;63(7):619-631. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2022.63.7.619. Yonsei Med J. 2022. PMID: 35748073 Free PMC article.
-
[Regulation of electroacupuncture on non-canonical pathway of hepatocellular pyroptosis in rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2024 May 12;44(5):539-45. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20230206-k0001. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2024. PMID: 38764104 Chinese.
-
[Effects of ellagic acid on inflammation and oxidative stress induced by AKT gene transfection in mice with fatty liver disease].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 May;44(9):1869-1875. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190228.001. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31342715 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Cultural and Molecular Factors Predisposed to Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Nutrients. 2025 May 26;17(11):1797. doi: 10.3390/nu17111797. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40507067 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aishwarya, V. , Solaipriya S., and Sivaramakrishnan V.. 2021. “Role of Ellagic Acid for the Prevention and Treatment of Liver Diseases.” Phytotherapy Research 35, no. 6: 2925–2944. - PubMed
-
- Aravinthan, A. , Scarpini C., Tachtatzis P., et al. 2013. “Hepatocyte Senescence Predicts Progression in Non‐alcohol‐Related Fatty Liver Disease.” Journal of Hepatology 58, no. 3: 549–556. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

