Burden of mental disorders and risk factors in the Western Pacific region from 1990 to 2021
- PMID: 39831008
- PMCID: PMC11684219
- DOI: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i1.101750
Burden of mental disorders and risk factors in the Western Pacific region from 1990 to 2021
Abstract
Background: The burden of mental disorders (MD) in the Western Pacific Region (WPR) remains a critical public health concern, with substantial variations across demographics and countries.
Aim: To analyze the burden of MD in the WPR from 1990 to 2021, along with associated risk factors, to reveal changing trends and emerging challenges.
Methods: We used data from the Global Burden of Disease 2021, analyzing prevalence, incidence, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) of MD from 1990 to 2021. Statistical methods included age-standardisation and uncertainty analysis to address variations in population structure and data completeness.
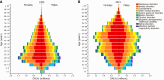
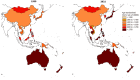
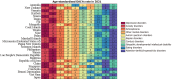
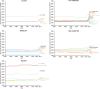
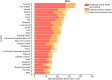
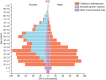
Results: Between 1990 and 2021, the prevalence of MD rose from 174.40 million cases [95% uncertainty interval (UI): 160.17-189.84] to 234.90 million cases (95%UI: 219.04-252.50), with corresponding DALYs increasing from 22.8 million (95%UI: 17.22-28.79) to 32.07 million (95%UI: 24.50-40.68). During this period, the burden of MD shifted towards older age groups. Depressive and anxiety disorders were predominant, with females showing higher DALYs for depressive and anxiety disorders, and males more affected by conduct disorders, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, and autism spectrum disorders. Australia, New Zealand, and Malaysia reported the highest burdens, whereas Vietnam, China, and Brunei Darussalam reported the lowest. Additionally, childhood sexual abuse and bullying, and intimate partner violence emerged as significant risk factors.
Conclusion: This study highlights the significant burden of MD in the WPR, with variations by age, gender, and nation. The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic has exacerbated the situation, emphasizing the need for a coordinated response.
Keywords: Disability-adjusted life years; Global Burden of Disease; Mental disorders; Risk factors; Western pacific region.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO in the Western Pacific. [cited 13 November 2024]. Available from: https://www.who.int/westernpacific/about .
-
- Castelpietra G, Knudsen AKS, Agardh EE, Armocida B, Beghi M, Iburg KM, Logroscino G, Ma R, Starace F, Steel N, Addolorato G, Andrei CL, Andrei T, Ayuso-Mateos JL, Banach M, Bärnighausen TW, Barone-Adesi F, Bhagavathula AS, Carvalho F, Carvalho M, Chandan JS, Chattu VK, Couto RAS, Cruz-Martins N, Dargan PI, Deuba K, da Silva DD, Fagbamigbe AF, Fernandes E, Ferrara P, Fischer F, Gaal PA, Gialluisi A, Haagsma JA, Haro JM, Hasan MT, Hasan SS, Hostiuc S, Iacoviello L, Iavicoli I, Jamshidi E, Jonas JB, Joo T, Jozwiak JJ, Katikireddi SV, Kauppila JH, Khan MAB, Kisa A, Kisa S, Kivimäki M, Koly KN, Koyanagi A, Kumar M, Lallukka T, Langguth B, Ledda C, Lee PH, Lega I, Linehan C, Loureiro JA, Madureira-Carvalho ÁM, Martinez-Raga J, Mathur MR, McGrath JJ, Mechili EA, Mentis AA, Mestrovic T, Miazgowski B, Mirica A, Mirijello A, Moazen B, Mohammed S, Mulita F, Nagel G, Negoi I, Negoi RI, Nwatah VE, Padron-Monedero A, Panda-Jonas S, Pardhan S, Pasovic M, Patel J, Petcu IR, Pinheiro M, Pollok RCG, Postma MJ, Rawaf DL, Rawaf S, Romero-Rodríguez E, Ronfani L, Sagoe D, Sanmarchi F, Schaub MP, Sharew NT, Shiri R, Shokraneh F, Sigfusdottir ID, Silva JP, Silva R, Socea B, Szócska M, Tabarés-Seisdedos R, Torrado M, Tovani-Palone MR, Vasankari TJ, Veroux M, Viner RM, Werdecker A, Winkler AS, Hay SI, Ferrari AJ, Naghavi M, Allebeck P, Monasta L. The burden of mental disorders, substance use disorders and self-harm among young people in Europe, 1990-2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2022;16:100341. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

