Metabolic pathway modulation by olanzapine: Multitarget approach for treating violent aggression in patients with schizophrenia
- PMID: 39831024
- PMCID: PMC11684224
- DOI: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i1.101186
Metabolic pathway modulation by olanzapine: Multitarget approach for treating violent aggression in patients with schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: The use of network pharmacology and blood metabolomics to study the pathogenesis of violent aggression in patients with schizophrenia and the related drug mechanisms of action provides new directions for reducing the risk of violent aggression and optimizing treatment plans.
Aim: To explore the metabolic regulatory mechanism of olanzapine in treating patients with schizophrenia with a moderate to high risk of violent aggression.
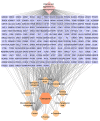
Methods: Metabolomic technology was used to screen differentially abundant metabolites in patients with schizophrenia with a moderate to high risk of violent aggression before and after olanzapine treatment, and the related metabolic pathways were identified. Network pharmacology was used to establish protein-protein interaction networks of the core targets of olanzapine. Gene Ontology functional analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis were subsequently performed.
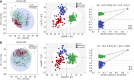
Results: Compared with the healthy group, the patients with schizophrenia group presented significant changes in the levels of 24 metabolites related to the disruption of 9 metabolic pathways, among which the key pathways were the alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism and arginine biosynthesis pathways. After treatment with olanzapine, the levels of 10 differentially abundant metabolites were significantly reversed in patients with schizophrenia. Olanzapine effectively regulated six metabolic pathways, among which the key pathways were alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism and arginine biosynthesis pathways. Ten core targets of olanzapine were involved in several key pathways.
Conclusion: The metabolic pathways of alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism and arginine biosynthesis are the key pathways involved in olanzapine treatment for aggressive schizophrenia.
Keywords: Metabolomics; Network pharmacology; Olanzapine; Schizophrenia; Violent aggression.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures





References
-
- Jauhar S, Johnstone M, McKenna PJ. Schizophrenia. Lancet. 2022;399:473–486. - PubMed
-
- Lindqvist P, Allebeck P. Schizophrenia and crime. A longitudinal follow-up of 644 schizophrenics in Stockholm. Br J Psychiatry. 1990;157:345–350. - PubMed
-
- Joyal C, Dubreucq J, Gendron C, Millaud F. Major Mental Disorders and Violence: A Critical Update. Curr Psychiat Rev. 2007;3:33–50.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

