The blind spots on chest computed tomography: what do we miss
- PMID: 39831206
- PMCID: PMC11740042
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-24-1125
The blind spots on chest computed tomography: what do we miss
Abstract
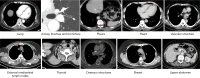
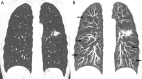
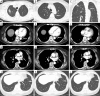
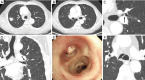
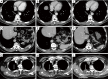
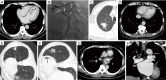
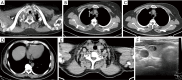
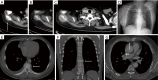
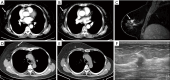
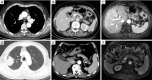
Chest computed tomography (CT) is the most frequently performed imaging examination worldwide. Compared with chest radiography, chest CT greatly improves the detection rate and diagnostic accuracy of chest lesions because of the absence of overlapping structures and is the best imaging technique for the observation of chest lesions. However, there are still frequently missed diagnoses during the interpretation process, especially in certain areas or "blind spots", which may possibly be overlooked by radiologists. Awareness of these blind spots is of great significance to avoid false negative results and potential adverse consequences for patients. In this review, we summarize the common blind spots identified in actual clinical practice, encompassing the central areas within the pulmonary parenchyma (including the perihilar regions, paramediastinal regions, and operative area after surgery), trachea and bronchus, pleura, heart, vascular structure, external mediastinal lymph nodes, thyroid, osseous structures, breast, and upper abdomen. In addition to careful review, clinicians can employ several techniques to mitigate or minimize errors arising from these blind spots in film interpretation and reporting. In this review, we also propose technical methods to reduce missed diagnoses, including advanced imaging post-processing techniques such as multiplanar reconstruction (MPR), maximum intensity projection (MIP), artificial intelligence (AI) and structured reporting which can significantly enhance the detection of lesions and improve diagnostic accuracy.
Keywords: Diagnostic imaging; blind spots; chest computed tomography (chest CT).
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-24-1125/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
