DesiRNA: structure-based design of RNA sequences with a replica exchange Monte Carlo approach
- PMID: 39831304
- PMCID: PMC11744100
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1306
DesiRNA: structure-based design of RNA sequences with a replica exchange Monte Carlo approach
Abstract
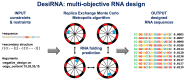
Designing RNA sequences that form a specific structure remains a challenge. Current computational methods often struggle with the complexity of RNA structures, especially when considering pseudoknots or restrictions related to RNA function. We developed DesiRNA, a computational tool for the design of RNA sequences based on the Replica Exchange Monte Carlo approach. It finds sequences that minimize a multiobjective scoring function, fulfill user-defined constraints and minimize the violation of restraints. DesiRNA handles pseudoknots, designs RNA-RNA complexes and sequences with alternative structures, prevents oligomerization of monomers, prevents folding into undesired structures and allows users to specify nucleotide composition preferences. In benchmarking tests, DesiRNA with a default simple scoring function solved all 100 puzzles in the Eterna100 benchmark within 24 h, outperforming all existing RNA design programs. With its ability to address complex RNA design challenges, DesiRNA holds promise for a range of applications in RNA research and therapeutic development.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Monte Carlo Inverse RNA Folding.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2847:205-215. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4079-1_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39312146
-
RNA inverse folding using Monte Carlo tree search.BMC Bioinformatics. 2017 Nov 6;18(1):468. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1882-7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 29110632 Free PMC article.
-
McGenus: a Monte Carlo algorithm to predict RNA secondary structures with pseudoknots.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Feb 1;41(3):1895-900. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1204. Epub 2012 Dec 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23248008 Free PMC article.
-
Design of RNAs: comparing programs for inverse RNA folding.Brief Bioinform. 2018 Mar 1;19(2):350-358. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbw120. Brief Bioinform. 2018. PMID: 28049135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in RNA folding.J Biotechnol. 2017 Nov 10;261:97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Jul 8. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28690134 Review.
Cited by
-
DRAG: design RNAs as hierarchical graphs with reinforcement learning.Brief Bioinform. 2025 Mar 4;26(2):bbaf106. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaf106. Brief Bioinform. 2025. PMID: 40079262 Free PMC article.
-
JAX-RNAfold: scalable differentiable folding.Bioinformatics. 2025 May 6;41(5):btaf203. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf203. Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40279486 Free PMC article.
-
Computational De Novo Design of Group II Introns Yields Highly Active Ribozymes.Chembiochem. 2025 Jul 18;26(14):e202500356. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202500356. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Chembiochem. 2025. PMID: 40504414 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive datasets for RNA design, machine learning, and beyond.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21417. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07041-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atkins J.F., Gesteland R.F., Cech T. RNA Worlds: From Life's Origins to Diversity in Gene Regulation. 2011; 2011:Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
-
- Sloma M.F., Zuker M., Mathews D.H.. Baxevanis A.D., Bader G.D., Wishart D.S. Predictive methods using RNA sequences. Bioinformatics. A Practical Guide to the Analysis of Genes and Proteins, 4th edition. 2020; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
-
- Hofacker I.L., Fontana W., Stadler P.F., Bonhoeffer L.S., Tacker M., Schuster P. Fast folding and comparison of RNA secondary structures. Monatsh. Chem. 1994; 125:167–188.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

