Detection and Whole Genome Amplification of the 4d Type of Porcine Hepatitis E Virus in Eastern Tibet, China
- PMID: 39832188
- PMCID: PMC11745153
- DOI: 10.1002/vms3.70194
Detection and Whole Genome Amplification of the 4d Type of Porcine Hepatitis E Virus in Eastern Tibet, China
Abstract
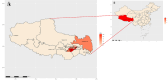
Genomic and evolutionary analysis of epidemic porcine hepatitis E virus (HEV) in the Tibetan Plateau was performed. Faecal samples were collected from 216 Tibetan pigs and 78 Tibetan Yorkshire (Large White) and 53 tissue samples from Yorkshire from the Linzhi City slaughterhouse. Total RNA was extracted from faeces and fragments of HEV open reading frame 2 (ORF2) detected by reverse transcription and nested polymerase chain reaction (RT-nPCR) and cloned. Twenty-three samples (23/347; 6.63%) were positive for the virus, including 6.94% (15/216) Tibetan pig and 6.11% (8/131) Yorkshire samples. No tissue samples tested positive for the virus. Cloned sequences were uploaded to GenBank (accession numbers: OR392679-OR392685, OR355817-OR355824 and OR909495-OR909502) and a phylogenetic tree constructed. The entire viral genome was amplified using primers for the 5-month-old Tibetan pig sequence which confirmed that the strain belonged to HEV type 4, subtype d (GenBank accession number: OQ981960) and showed 93.30% homology with Sichuan Tibetan pig sequence, MK410044. Bayesian tree analysis showed that the earliest divergence was in 1999 and evidence of homologous recombination was found. Genomic and evolutionary analysis of HEV in the Tibetan Plateau is presented. The importance of continuous surveillance and genomic analysis of HEV is highlighted, especially in regions like the Tibetan Plateau where new strains may emerge. The findings contribute to our understanding of HEV's genetic diversity, evolutionary history and potential risks to animal and human health.
Keywords: Tibetan pig; detection; genome evolutionary characterisation; hepatitis E virus; whole gene amplification.
© 2025 The Author(s). Veterinary Medicine and Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

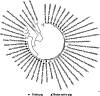
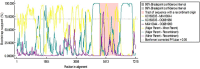
 Yorkie pig; ▴ Tibetan native pigs. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using MegA 7 software for 23 positive samples of HEV ORF2 (348 bp) from Tibetan pigs. Phylogenetic analysis showed the 23 strains to belong to the same branch as HEV‐4d Yunnan cow KY233432 isolate. The results revealed that Tibetan pig HEV was type 4d.
Yorkie pig; ▴ Tibetan native pigs. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using MegA 7 software for 23 positive samples of HEV ORF2 (348 bp) from Tibetan pigs. Phylogenetic analysis showed the 23 strains to belong to the same branch as HEV‐4d Yunnan cow KY233432 isolate. The results revealed that Tibetan pig HEV was type 4d.

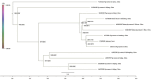
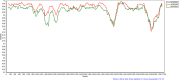
 OQ981960; ▴ Type HEV‐4d. A phylogenetic tree was constructed for Tibetan pig OQ981960 using MegA 7 software, related to HEV MK410044 isolated from Tibetan pigs in Sichuan Province in 2018 and HEV KC163335 isolated from human infection in Shandong Province in 2012. The results revealed that Tibetan pig HEV OQ981960 was type 4d.
OQ981960; ▴ Type HEV‐4d. A phylogenetic tree was constructed for Tibetan pig OQ981960 using MegA 7 software, related to HEV MK410044 isolated from Tibetan pigs in Sichuan Province in 2018 and HEV KC163335 isolated from human infection in Shandong Province in 2012. The results revealed that Tibetan pig HEV OQ981960 was type 4d.
References
-
- Ga, G. , and Sizhu S.. 2020. “Molecular Detection of Hepatitis E Virus in Tibetan Swine.” Pakistan Journal of Zoology 52: 1563–1569.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

