De novo transcriptome assembly of the Mediterranean sea-rock pool mosquitoes Aedes mariae and Aedes zammitii
- PMID: 39833234
- PMCID: PMC11746941
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-025-04393-2
De novo transcriptome assembly of the Mediterranean sea-rock pool mosquitoes Aedes mariae and Aedes zammitii
Abstract
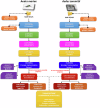
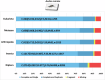
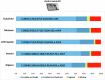
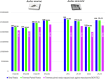
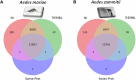
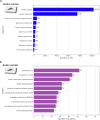
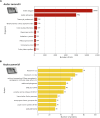
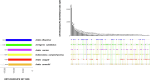
Understanding the genomic consequences of hybridization is an essential research focus in global change biology. Species adapted to rapidly changing environments can offer valuable, yet largely underexplored insights in this context. Here, we present the first de novo transcriptomes of the sea-rock pools mosquitoes Aedes mariae and Aedes zammitii, two species adapted to highly variable habitats. Using RNA-seq data obtained from larval stages, we assembled and annotated 95,059,578 reads for Ae. mariae and 101,050,236 reads for Ae. zammitii, detecting 49,352 transcripts with N50 of 2,615 for the former and 43,461 transcripts with N50 of 2,570 for the latter. Validation by BUSCO confirmed the high quality of our resources. Homology alignments of predicted ORFs showed that 21,842 sequences from Ae. mariae and 21,944 sequences from Ae. zammitii mapped to the Nr, SwissProt, and TrEMBL databases, while 19,208 and 19,393 predicted ORFs, respectively, were functionally annotated using the COG and KEGG databases. These high-quality transcriptomes will provide valuable resources to investigate the role of hybridization in species adaptation to changing environments.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distribution pattern and genetic structure of Aedes zammitii (Diptera: Culicidae) along the Mediterranean and Aegean coasts of Turkey.J Vector Ecol. 2016 Jun;41(1):151-9. doi: 10.1111/jvec.12207. J Vector Ecol. 2016. PMID: 27232138
-
Genetic distance between two sibling species of the Aedes mariae complex (Diptera, Culicidae).Parassitologia. 1978 Dec;20(1-3):39-46. Parassitologia. 1978. PMID: 553279
-
Larvae ecology and adult activity of Aedes mariae (Diptera: Culicidae) in a touristic rock-pool area of the Balearic Islands (Western Mediterranean).Bull Entomol Res. 2021 Dec 9:1-8. doi: 10.1017/S0007485321001024. Online ahead of print. Bull Entomol Res. 2021. PMID: 34881694
-
Integrated de novo transcriptome of Culex pipiens mosquito larvae as a resource for genetic control strategies.Sci Data. 2024 May 9;11(1):471. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03285-1. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38724521 Free PMC article.
-
The transcriptome of the mosquito Aedes fluviatilis (Diptera: Culicidae), and transcriptional changes associated with its native Wolbachia infection.BMC Genomics. 2017 Jan 3;18(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3441-4. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28049478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott, R. et al. Hybridization and speciation. J Evol Biol.26, 229–246 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Grabenstein, K. C. & Taylor, S. A. Breaking Barriers: Causes, Consequences, and Experimental Utility of Human-Mediated Hybridization. Trends Ecol Evol.33, 198–212 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Porretta, D. & Canestrelli, D. The ecological importance of hybridization. Trends Ecol Evol.38, 1097–1108 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Barton, N. H. & Hewitt, G. M. Analysis of Hybrid Zones. Ann Rev Ecol Evol Syst.16, 113–148 (1985).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

