Mapping the cellular etiology of schizophrenia and complex brain phenotypes
- PMID: 39833308
- PMCID: PMC11802450
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01834-w
Mapping the cellular etiology of schizophrenia and complex brain phenotypes
Abstract
Psychiatric disorders are multifactorial and effective treatments are lacking. Probable contributing factors to the challenges in therapeutic development include the complexity of the human brain and the high polygenicity of psychiatric disorders. Combining well-powered genome-wide and brain-wide genetics and transcriptomics analyses can deepen our understanding of the etiology of psychiatric disorders. Here, we leverage two landmark resources to infer the cell types involved in the etiology of schizophrenia, other psychiatric disorders and informative comparison of brain phenotypes. We found both cortical and subcortical neuronal associations for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. These cell types included somatostatin interneurons, excitatory neurons from the retrosplenial cortex and eccentric medium spiny-like neurons from the amygdala. In contrast we found T cell and B cell associations with multiple sclerosis and microglial associations with Alzheimer's disease. We provide a framework for a cell-type-based classification system that can lead to drug repurposing or development opportunities and personalized treatments. This work formalizes a data-driven, cellular and molecular model of complex brain disorders.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: K.D. is a founder and scientific advisor for Maplight Therapeutics and Stellaromics, and a scientific advisor to RedTree LLC and Modulight.
Figures



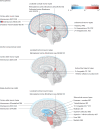


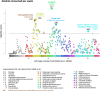



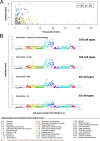
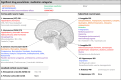
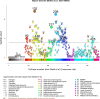
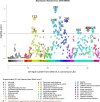

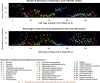
Comment in
-
Identification of neurons involved in schizophrenia.Nat Rev Neurol. 2025 Mar;21(3):125. doi: 10.1038/s41582-025-01067-w. Nat Rev Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39962297 No abstract available.
References
-
- 2021 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2021); https://www.samhsa.gov/data/report/2021-nsduh-annual-national-report - PubMed
-
- Kadakia, A. et al. The economic burden of schizophrenia in the United States. J. Clin. Psychiatry83, 22m14458 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Tandon, R., Keshavan, M. S. & Nasrallah, H. A. Schizophrenia, “just the facts” what we know in 2008. 2. Epidemiology and etiology. Schizophr. Res.102, 1–18 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Hilker, R. et al. Heritability of schizophrenia and schizophrenia spectrum based on the nationwide Danish Twin Register. Biol. Psychiatry83, 492–498 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Cardno, A. G. et al. Heritability estimates for psychotic disorders: the Maudsley twin psychosis series. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry56, 162–168 (1999). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

