Positively charged cytoplasmic residues in corin prevent signal peptidase cleavage and endoplasmic reticulum retention
- PMID: 39833422
- PMCID: PMC11756421
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-07545-7
Positively charged cytoplasmic residues in corin prevent signal peptidase cleavage and endoplasmic reticulum retention
Abstract
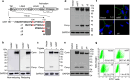
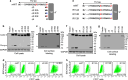
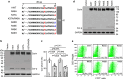
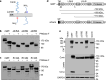
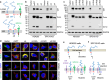
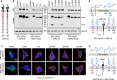
Positively charged residues are commonly located near the cytoplasm-membrane interface, which is known as the positive-inside rule in membrane topology. The mechanism underlying the function of these charged residues remains poorly understood. Herein, we studied the function of cytoplasmic residues in corin, a type II transmembrane serine protease in cardiovascular biology. We found that the positively charged residue at the cytoplasm-membrane interface of corin was not a primary determinant in membrane topology but probably served as a charge-repulsion mechanism in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to prevent interactions with proteins in the ER, including the signal peptidase. Substitution of the positively charged residue with a neutral or acidic residue resulted in corin secretion likely due to signal peptidase cleavage. In signal peptidase-deficient cells, the mutant corin proteins were not secreted but retained in the ER. Similar results were found in the low-density lipoprotein receptor and matriptase-2 that have positively charged residues at and near the cytoplasm-membrane interface. These results provide important insights into the role of the positively charged cytoplasmic residues in mammalian single-pass transmembrane proteins.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel cytoplasmic tail motif regulates mouse corin expression on the cell surface.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Sep 11;465(1):152-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.07.156. Epub 2015 Aug 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26241673 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of the hepatitis B virus precore protein to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane: after signal peptide cleavage translocation can be aborted and the product released into the cytoplasm.J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1093-104. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1093. J Cell Biol. 1988. PMID: 3283145 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of corin protein domains required for PCSK6-mediated activation.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018 Jan;94:31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2017.11.010. Epub 2017 Nov 24. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29180304 Free PMC article.
-
The serine protease corin in cardiovascular biology and disease.Front Biosci. 2007 May 1;12:4179-90. doi: 10.2741/2379. Front Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17485366 Review.
-
Bacterial Signal Peptidases.Subcell Biochem. 2019;92:187-219. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-18768-2_7. Subcell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31214988 Review.
References
-
- Fagerberg, L., Jonasson, K., von Heijne, G., Uhlén, M. & Berglund, L. Prediction of the human membrane proteome. Proteomics10, 1141–1149 (2010). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

