Serotonin receptor 5-HT7 modulates inflammatory-associated functions of macrophages
- PMID: 39833622
- PMCID: PMC11747067
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-024-05570-z
Serotonin receptor 5-HT7 modulates inflammatory-associated functions of macrophages
Abstract
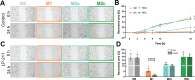
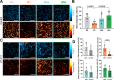
The hormone and neurotransmitter serotonin regulates numerous physiological functions within the central nervous system and in the periphery upon binding to specific receptors. In the periphery, the serotonin receptor 7 (5-HT7R) is expressed on different immune cells including monocytes and macrophages. To investigate the impact of 5-HT7R-mediated signaling on macrophage properties, we used human THP-1 cells and differentiated them into pro-inflammatory M1- and anti-inflammatory M2-like macrophages. Pharmacological 5-HT7R activation with the specific agonist LP-211 especially modulates morphology of M1-like macrophages by increasing the number of rounded cells. Furthermore, 5-HT7R stimulation results in significantly reduced phagocytic and migratory ability of M1-like macrophages. Noteworthy, LP-211 treatment leads to changes in secretory properties of all macrophage types with the highest effects obtained for M0- and M2c-like macrophages. Finally, the importance of 5-HT7R for regulation of phagocytosis was confirmed in human primary CD14+ cells. These results indicate that 5-HT7R activation selectively impairs basic functions of macrophages and might thus be a new access point for the modulation of macrophage responses in the future treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: 5-HT7 receptor; Macrophages; Phagocytosis; Serotonin; THP-1 cells.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: Not applicable. Consent for publication: The authors hereby consent to publication of the work in Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- El-Merahbi R, Löffler M, Mayer A, Sumara G (2015) The roles of peripheral serotonin in metabolic homeostasis. FEBS Lett 589:1728–1734. 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.05.054 - PubMed
-
- Sharp T, Barnes NM (2020) Central 5-HT receptors and their function; present and future. Neuropharmacology 177:108155. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108155 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

