The efficacy and safety of patient-controlled intravenous analgesia with esketamine after total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 39833672
- PMCID: PMC11744849
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-025-02894-6
The efficacy and safety of patient-controlled intravenous analgesia with esketamine after total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of esketamine-based patient-controlled intravenous analgesia following total hip arthroplasty.
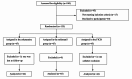
Methods: A total of 135 total hip arthroplasty patients were randomly assigned to one of the three treatment groups: esketamine, sufentanil or continuous fascia iliaca compartment block (FICB) group. The primary endpoint was the postoperative visual analogue scale (VAS) pain scores at rest and on movement. Secondary endpoints included preoperative 1-day and postoperative 7-day Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) and Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) scores, the satisfaction of patients and surgeons, postoperative 1-month and 3-month Harris function scores, the incidence of adverse reactions.
Results: At 48 h post-surgery, the VAS pain scores in the esketamine and FICB groups at rest and on movement were significantly lower than those in the sufentanil group (P < 0.05). The satisfaction of patients in the esketamine group was higher than that in the sufentanil and FICB groups (P = 0.014). The satisfaction of surgeons in the esketamine and FICB groups was higher than that in the sufentanil group (P = 0.002). At postoperative day 7, the SAS scores and SDS scores in the esketamine group were significantly lower than those in the sufentanil and FICB groups (P < 0.05). Compared with the sufentanil group, the postoperative nausea and vomiting, dizziness and total adverse reactions in the esketamine group and FICB group were lower (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Patient-controlled intravenous analgesia with esketamine has the potential to provide good postoperative analgesia for total hip arthroplasty patients, reduce the incidence of adverse reactions after the operation, improve the satisfaction of patients and surgeons, and significantly improve patients' postoperative mood.
Trial registration: ChiCTR2300069632 ( https://www.chictr.org.cn/ ) (March 22th, 2023).
Keywords: Esketamine; Fascia Iliaca compartment block; Patient controlled intravenous analgesia; Postoperative pain; Total hip arthroplasty.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval and consent to Participate: This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committees of Gansu Provincial Hospital (Ethical code: 2022 − 423) and was registered at the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry ( https://www.chictr.org.cn/ , identifier: ChiCTR2300069632) on March 22th, 2023. Written informed consent was obtained from the patients to publish this article in accordance with the journal’s patient consent policy. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declarations of Helsinki, and adhered to the CONSORT guidelines. Consent for publication: N/A. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
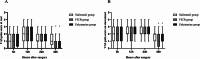
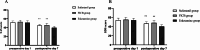
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

