Synthesis and Investigation of Peptide-Drug Conjugates Comprising Camptothecin and a Human Protein-Derived Cell-Penetrating Peptide
- PMID: 39834140
- PMCID: PMC11747586
- DOI: 10.1111/cbdd.70051
Synthesis and Investigation of Peptide-Drug Conjugates Comprising Camptothecin and a Human Protein-Derived Cell-Penetrating Peptide
Abstract
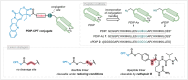
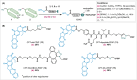
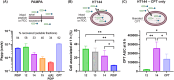
Drug targeting strategies, such as peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs), have arisen to combat the issue of off-target toxicity that is commonly associated with chemotherapeutic small molecule drugs. Here we investigated the ability of PDCs comprising a human protein-derived cell-penetrating peptide-platelet factor 4-derived internalization peptide (PDIP)-as a targeting strategy to improve the selectivity of camptothecin (CPT), a topoisomerase I inhibitor that suffers from off-target toxicity. The intranuclear target of CPT allowed exploration of PDC design features required for optimal potency. A suite of PDCs with various structural characteristics, including alternative conjugation strategies (such as azide-alkyne cycloaddition and disulfide conjugation) and linker types (non-cleavable or cleavable), were synthesized and investigated for their anticancer activity. Membrane permeability and cytotoxicity studies revealed that intact PDIP-CPT PDCs can cross membranes, and that PDCs with disulfide- and protease-cleavable linkers liberated free CPT and killed melanoma cells with nanomolar potency. However, selectivity of the PDIP carrier peptide for melanoma compared to noncancerous epidermal cells was not maintained for the PDCs. This study emphasizes the distinct role of the peptide, linker, and drug for optimal PDC activity and highlights the need to carefully match components when assembling PDCs as targeted therapies.
Keywords: camptothecin; cell‐penetrating peptide; cleavable linker; melanoma; peptide–drug conjugate.
© 2025 The Author(s). Chemical Biology & Drug Design published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Design and synthesis of TH19P01-Camptothecin based hybrid peptides inducing effective anticancer responses on sortilin positive cancer cells.Bioorg Med Chem. 2024 Sep 1;111:117869. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2024.117869. Epub 2024 Aug 3. Bioorg Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39126834
-
The development of peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs) strategies for paclitaxel.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2022 Feb;19(2):147-161. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2022.2039621. Epub 2022 Feb 13. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35130795 Review.
-
Improving anticancer activity and selectivity of camptothecin through conjugation with releasable substance P.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Mar 1;21(5):1452-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.01.013. Epub 2011 Jan 8. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011. PMID: 21282053
-
Synthesis and Antiproliferative Activities of Conjugates of Paclitaxel and Camptothecin with a Cyclic Cell-Penetrating Peptide.Molecules. 2019 Apr 11;24(7):1427. doi: 10.3390/molecules24071427. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30978971 Free PMC article.
-
Current progress and remaining challenges of peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs): next generation of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs)?J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Apr 22;23(1):305. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03277-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40259322 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CE200100012/Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Innovations in Peptide and Protein Science
- W81XWH2210219/US Department of Defense Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs
- GNT2009564/National Health and Medical Research Council
- Australian Government Research Training Program PhD Scholarship scheme
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

