Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: Pathophysiology and Treatment Modalities
- PMID: 39834999
- PMCID: PMC11743060
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.75992
Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: Pathophysiology and Treatment Modalities
Abstract
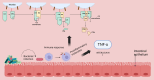
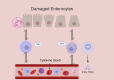
Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (S-AKI) is a critical complication that significantly contributes to the morbidity and mortality of sepsis patients. This narrative review explores the complex and multifactorial pathophysiology of S-AKI, which involves hemodynamic alterations, microcirculatory dysfunction, endothelial damage, inflammatory responses, oxidative stress, and direct tubular injury. Conventional perspectives linking S-AKI primarily to reduced renal blood flow are now being reconsidered, with growing insights highlighting the significance of microcirculatory dysfunction and endothelial activation as key contributors. The review also discusses the current diagnostic approaches for S-AKI, emphasizing the limitations of existing biomarkers and the need for earlier and more accurate detection methods. Standard treatment strategies focus on supportive care, including fluid management, vasopressor therapy, and renal replacement therapy. However, these approaches often fail to address the underlying mechanisms of S-AKI, resulting in persistently high mortality rates. Emerging therapies, including the use of antioxidants, anti-inflammatory agents, and stem cell-based treatments, offer the potential for improved outcomes. These innovative approaches aim to target the pathophysiological processes at the molecular level, offering hope for better management of S-AKI. The review highlights the need for ongoing research to further understand the mechanisms driving S-AKI and to develop more effective therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: cytokine storm; emerging therapies; endothelial activation; fluid management; inflammatory response; microcirculatory dysfunction; oxidative stress; renal replacement therapy; s-aki pathophysiology; sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.
Copyright © 2024, Aguilar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Sepsis: pathophysiology and clinical management. Gotts JE, Matthay MA. BMJ. 2016;353:0. - PubMed
-
- Acute kidney injury . Ronco C, Bellomo R, Kellum JA. Lancet. 2019;394:1949–1964. - PubMed
-
- Intrarenal and urinary oxygenation during norepinephrine resuscitation in ovine septic acute kidney injury. Lankadeva YR, Kosaka J, Evans RG, Bailey SR, Bellomo R, May CN. Kidney Int. 2016;90:100–108. - PubMed
-
- Renal perfusion in sepsis: from macro- to microcirculation. Post EH, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Vincent JL. Kidney Int. 2017;91:45–60. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
