Association Between SHBG Levels and Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39835844
- PMCID: PMC11771790
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.14977
Association Between SHBG Levels and Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
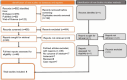
Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) regulates sex hormone availability and is influenced by metabolic factors. Variations in SHBG levels during pregnancy may affect the development of hypertensive disorders such as gestational hypertension (GH) and preeclampsia (PE). This systematic review and meta-analysis explores the potential of SHBG as a biomarker for predicting GH and PE. A search of PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science was conducted to identify studies evaluating the association between SHBG levels and the risk of HDP, including GH and PE. Inclusion criteria encompassed observational studies reporting quantitative risk estimates (risk ratios, odds ratios, or hazard ratios) for SHBG levels. Results were pooled using a random-effects meta-analysis in R software (V 4.4), with the I2 statistic assessing heterogeneity. Eight studies were included in the systematic review from a total of 592 screened records. The association between SHBG levels and the risk of any HDP showed a pooled OR of 0.875 (95% CI: 0.772-0.993), for PE 0.890 (95% CI: 0.767-1.032), and for GH 0.729 (95% CI: 0.442-1.205), suggesting significant association between SHBG and HDP. Sensitivity analysis validated the robustness of the findings. This meta-analysis found potential significant association between higher SHBG levels and risk of HDP. Further high-quality research is required to better understand the role of SHBG in pregnancy-related hypertensive disorders. Future studies should consider larger sample sizes, more precise measurement techniques, and explore potential confounding factors to clarify the potential utility of SHBG as a biomarker for predicting GH and PE.
Keywords: gestational hypertension; hypertensive disorders of pregnancy; preeclampsia; pregnancy biomarker; sex hormone binding globulin.
© 2025 The Author(s). The Journal of Clinical Hypertension published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Exploring the link between sex hormone-binding globulin levels and prostate cancer risk: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Jun;57(6):1673-1687. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04370-z. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39786704
-
The association between dietary factors and gestational hypertension and pre-eclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.BMC Med. 2014 Sep 22;12:157. doi: 10.1186/s12916-014-0157-7. BMC Med. 2014. PMID: 25241701 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy after multifetal pregnancy reduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Hypertens Pregnancy. 2023 Dec;42(1):2225597. doi: 10.1080/10641955.2023.2225597. Hypertens Pregnancy. 2023. PMID: 37337887
-
Planned early delivery versus expectant management for hypertensive disorders from 34 weeks gestation to term.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 15;1(1):CD009273. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009273.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28106904 Free PMC article.
-
Sex as a prognostic factor for mortality in adults with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Mar 20;3(3):CD013835. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013835.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40110896
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Review of Current Advancements in the Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Implications of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy.Cureus. 2025 May 29;17(5):e85025. doi: 10.7759/cureus.85025. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40585732 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mukherjee A. G. and Gopalakrishnan A. V., “Sex Hormone‐Binding Globulin and Its Critical Role in Prostate Cancer: A Comprehensive Review,” The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 245 (2025): 106606. - PubMed
-
- Bourebaba N., Ngo T., Śmieszek A., Bourebaba L., and Marycz K., “Sex Hormone Binding Globulin as a Potential Drug Candidate for Liver‐Related Metabolic Disorders Treatment,” Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 153 (2022): 113261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

