Randomized Phase II Study of Bevacizumab with Weekly Anetumab Ravtansine or Weekly Paclitaxel in Platinum-Resistant/Refractory High-Grade Ovarian Cancer (NCI Trial)
- PMID: 39836408
- PMCID: PMC11911801
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-3128
Randomized Phase II Study of Bevacizumab with Weekly Anetumab Ravtansine or Weekly Paclitaxel in Platinum-Resistant/Refractory High-Grade Ovarian Cancer (NCI Trial)
Abstract
Purpose: Mesothelin (MSLN) is highly expressed in high-grade serous/endometrioid ovarian cancers (HGOC). Anetumab ravtansine (AR) is an antibody-drug conjugate directed at the MSLN antigen with a tubulin polymerization inhibitor. We assessed the safety, activity, and pharmacokinetics of the combination AR/bevacizumab (Bev; ARB) versus weekly paclitaxel/Bev (PB) in patients with platinum-resistant/refractory HGOC (prrHGOC).
Patients and methods: Following a run-in phase I study to assess ARB safety, patients with prrHGOC with centrally confirmed MSLN-positive expression were randomized to ARB or PB (weekly paclitaxel 80 mg/m2 with Bev 10 mg/kg biweekly). Patients were stratified by platinum resistance/refractory and prior Bev. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS), and secondary endpoints were overall response rate, safety, and blood-based angiome biomarker assessment. A futility analysis was planned after 35 PFS events.
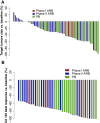
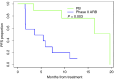
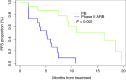
Results: The combination of Bev (10 mg/kg) biweekly with AR (2.2 mg/kg) weekly was well tolerated. About phase II results, MSLN positivity was 88%, and 57 patients were randomized (28 ARB and 29 PB). Forty-two percentage of patients received prior Bev, and 23% were platinum-refractory. At futility analysis, the median PFS was 5.3 and 12.7 months for ARB and PB, respectively [P = 0.03; HR = 2.02 (1.06-3.86)]. The overall response rate was 21% with ARB and 65% with PB. The most common treatment-related grade ≥3 adverse events were anemia (18%) with ARB and neutropenia (24%) with PB. Higher baseline levels of circulating IL6 were associated with worse PFS, and its levels decreased with PB treatment.
Conclusions: Our study stopped at interim analysis highlighting the benefit of PB in prrHGOC as the standard of care.
©2025 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
J.-Y. Chern reports other support from AstraZeneca, American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Equinox Group, The Dedham Group, Association of Cancer Care Centers, IDEOlogy Health, Cardinal Health, Reckner Health, and Techspert outside the submitted work. L.R. Duska reports grants from sponsored trials; other support from Inovio, Agenus, and Merck advisory board; and personal fees from Daiichi Sankyo outside the submitted work. B.R. Corr reports other support from ImmunoGen, Clovis, GSK, ImmunoGen/AbbVie, Merck, Eisai, and Gilead outside the submitted work. M.A. Crispens reports grants from the NCI during the conduct of the study. A. Madariaga reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, AbbVie, GSK, PharmaMar, Pharma&, and MSD during the conduct of the study. R.C. Grant reports personal fees from AstraZeneca; nonfinancial support from Tempus; and personal fees from Eisai, Incyte, Knight Therapeutics, Guardant Health, and Ipsen outside the submitted work. P.L. Bedard reports grants from AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Medicenna, LegoChem, Roche/Genentech, Pfizer, Merck, Zymeworks, Novartis, Gilead, Lilly, Takeda, and Bicara outside the submitted work and uncompensated advisory for Janssen, Repare, Roche, Lilly, Seagen/Pfizer, and Zymeworks. A.B. Nixon reports grants from Genentech, Genmab, MedImmune/AstraZeneca, and Seagen/Pfizer and personal fees from LeapTherapuetics, Sanofi, and Promega outside the submitted work. W. Zamboni reports grants from NCI during the conduct of the study. A.M. Oza reports other support from AstraZeneca, personal fees and other support from GSK, and other support from Pharma&, PharmaMar, and Merck Sharp & Dohme outside the submitted work. S. Lheureux reports grants and personal fees from GSK, AstraZeneca, Roche, Seagen, Repare, Schrodinger, Eisai, and Merck, as well as personal fees from Gilead, Abbvie, and Zai Lab outside the submitted work. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures


References
-
- Pujade-Lauraine E, Hilpert F, Weber B, Reuss A, Poveda A, Kristensen G, et al. . Bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy for platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer: the AURELIA open-label randomized phase III trial. Obstetrical Gynecol Surv 2014;69:402–4. - PubMed
-
- Poveda AM, Selle F, Hilpert F, Reuss A, Savarese A, Vergote I, et al. . Bevacizumab combined with weekly paclitaxel, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, or topotecan in platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer: analysis by chemotherapy cohort of the randomized phase III AURELIA trial. J Clin Oncol 2015;33:3836–8. - PubMed
-
- Pignata S, Lorusso D, Joly F, Gallo C, Colombo N, Sessa C, et al. . Carboplatin-based doublet plus bevacizumab beyond progression versus carboplatin-based doublet alone in patients with platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer: a randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2021;22:267–76. - PubMed
-
- Kerbel RS, Kamen BA. The anti-angiogenic basis of metronomic chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2004;4:423–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

