Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury: from Mechanistic Insights to Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 39836498
- PMCID: PMC11923913
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202413364
Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury: from Mechanistic Insights to Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
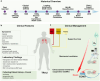
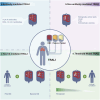
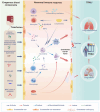
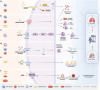
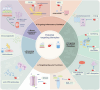
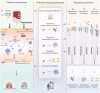
Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) is a potentially lethal complication of blood transfusions, characterized by the rapid onset of pulmonary edema and hypoxemia within six hours post-transfusion. As one of the primary causes of transfusion-related mortality, TRALI carries a significant mortality rate of 6-12%. However, effective treatment strategies for TRALI are currently lacking, underscoring the urgent need for a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of its pathogenesis. This comprehensive review provides an updated and detailed analysis of the current landscape of TRALI, including its clinical presentation, pathogenetic hypotheses, animal models, cellular mechanisms, signaling pathways, and potential therapeutic targets. By highlighting the critical roles of these pathways and therapies, this review offers valuable insights to inform the development of preventative and therapeutic strategies and to guide future research efforts aimed at addressing this life-threatening condition.
Keywords: immune response; pathogenesis; signaling pathways; therapeutic strategies; transfusion‐related acute lung injury (TRALI).
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Popovsky M. A., Abel M. D., Moore S. B., Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1983, 128, 185. - PubMed
-
- Kleinman S., Caulfield T., Chan P., Davenport R., McFarland J., McPhedran S., Meade M., Morrison D., Pinsent T., Robillard P., Slinger P., Transfusion 2004, 44, 1774. - PubMed
-
- Barnard R. D., N. Y. State J. Med. 1951, 51, 2399. - PubMed
-
- Popovsky M. A., Moore S. B., Transfusion 1985, 25, 573. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
