Ultrasensitive 129Xe Magnetic Resonance Imaging: From Clinical Monitoring to Molecular Sensing
- PMID: 39836636
- PMCID: PMC12083861
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202413426
Ultrasensitive 129Xe Magnetic Resonance Imaging: From Clinical Monitoring to Molecular Sensing
Abstract
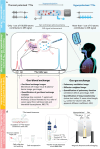
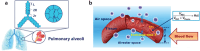
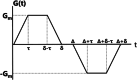
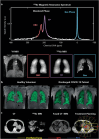
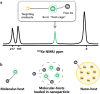
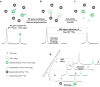
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone technology in clinical diagnostics and in vivo research, offering unparalleled visualization capabilities. Despite significant advancements in the past century, traditional 1H MRI still faces sensitivity limitations that hinder its further development. To overcome this challenge, hyperpolarization methods have been introduced, disrupting the thermal equilibrium of nuclear spins and leading to an increased proportion of hyperpolarized spins, thereby enhancing sensitivity by hundreds to tens of thousands of times. Among these methods, hyperpolarized (HP) 129Xe MRI, also known as ultrasensitive 129Xe MRI, stands out for achieving the highest polarization enhancement and has recently received clinical approval. It effectively tackles the challenge of weak MRI signals from low proton density in the lungs. HP 129Xe MRI is valuable for assessing structural and functional changes in lung physiology during pulmonary disease progression, tracking cells, and detecting target molecules at pico-molar concentrations. This review summarizes recent developments in HP 129Xe MRI, including its physical principles, manufacturing methods, in vivo characteristics, and diverse applications in biomedical, chemical, and material sciences. In addition, it carefully discusses potential technical improvements and future prospects for enhancing its utility in these fields, further establishing HP 129Xe MRI's importance in advancing medical imaging and research.
Keywords: biosensors; hyperpolarization; magnetic resonance imaging; nanomaterials; the lungs.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
