Association of Liver Fibrosis Markers with Mortality Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from the NHANES 1999-2018 Data
- PMID: 39837280
- PMCID: PMC11844702
- DOI: 10.1159/000543500
Association of Liver Fibrosis Markers with Mortality Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from the NHANES 1999-2018 Data
Abstract
Introduction: The objective of this research was to explore the possible link between markers of liver fibrosis and survival rates in a group of adults who have been diagnosed with both chronic kidney disease (CKD) and coronary artery disease (CAD).
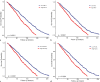
Methods: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data (1999-2018) for participants with both CAD and CKD were analyzed. The fibrosis-4 index (FIB-4), Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Score (NFS), Forns index, and aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase (AST/ALT) ratio were identified as crucial biomarkers. All-cause and cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality were primary outcomes, assessed using Cox models, Kaplan-Meier curves, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis.
Results: A total of 1,192 CKD and CAD patients were included. The Cox regression analysis revealed substantial correlations between elevated FIB-4, NFS, Forns index, and AST/ALT levels and a heightened risk of all-cause (hazard ratio [HR]: 1.188, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.108-1.274; HR: 1.145, 95% CI: 1.069-1.227; HR: 1.142, 95% CI: 1.081-1.201; HR: 1.316, 95% CI: 1.056-1.639, respectively) and CVD mortality (HR: 1.133, 95% CI: 1.007-1.275; HR: 1.155, 95% CI: 1.024-1.303; HR: 1.208, 95% CI: 1.109-1.316 and HR: 1.636, 95% CI: 1.203-2.224, respectively). The ROC analysis indicated comparable predictive accuracy for all three biomarkers, with AST/ALT showing slightly superior performance.
Conclusion: Liver fibrosis markers, including AST/ALT, NFS, Forns index and FIB-4, are significant mortality predictors in CAD-CKD patients. The AST/ALT ratio, being easily measurable, may serve as an effective predictive tool for risk stratification in this population.
Keywords: AST/ALT ratios; Chronic kidney disease; Coronary artery disease; Liver fibrosis markers; Mortality.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Sarnak MJ, Amann K, Bangalore S, Cavalcante JL, Charytan DM, Craig JC, et al. Chronic kidney disease and coronary artery disease: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74(14):1823–38. - PubMed
-
- Ndumele CE, Neeland IJ, Tuttle KR, Chow SL, Mathew RO, Khan SS, et al. A synopsis of the evidence for the science and clinical management of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome: a scientific statement from the American heart association. Circulation. 2023;148(20):1636–64. - PubMed
-
- Farkouh ME, Sidhu MS, Brooks MM, Vlachos H, Boden WE, Frye RL, et al. Impact of chronic kidney disease on outcomes of myocardial revascularization in patients with diabetes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(4):400–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

