Machine learning based prediction models for the prognosis of COVID-19 patients with DKA
- PMID: 39837852
- PMCID: PMC11751332
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-85357-9
Machine learning based prediction models for the prognosis of COVID-19 patients with DKA
Abstract
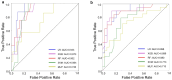
Patients with Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) have increased critical illness and mortality during coronavirus diseases 2019 (COVID-19). The aim of our study was to develop a predictive model for the occurrence of critical illness and mortality in COVID-19 patients with DKA utilizing machine learning. Blood samples and clinical data from 242 COVID-19 patients with DKA collected from December 2022 to January 2023 at Second Xiangya Hospital. Patients were categorized into non-death (n = 202) and death (n = 38) groups, and non-severe (n = 146) and severe (n = 96) groups. We developed five machine learning-based prediction models-Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGB), Logistic Regression (LR), Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machine (SVM), and Multilayer Perceptron (MLP)-to evaluate the prognosis of COVID-19 patients with DKA. We employed 5-fold cross-validation for model evaluation and used the Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) algorithm for result interpretation to ensure reliability. The LR model demonstrated the highest accuracy (AUC = 0.933) in predicting mortality. Additionally, the LR model excelled (AUC = 0.898) in predicting progression to severe disease. This study developed a machine learning-based predictive model for the progression to severe disease or death in COVID-19 patients with DKA, which can serve as a valuable tool to guide clinical treatment decisions.
Keywords: COVID-19; Diabetes; Ketoacidosis; Machine learning; Prediction.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Nyenwe, E. A. & Kitabchi, A. E. The evolution of diabetic ketoacidosis: an update of its etiology, pathogenesis and management. Metabolism65, 507–521. 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.12.007 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Birkebaek, N. H. et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on long-term trends in the prevalence of diabetic ketoacidosis at diagnosis of paediatric type 1 diabetes: an international multicentre study based on data from 13 national diabetes registries. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.10, 786–794. 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00246-7 (2022). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

