Prognostic value of CT-based skeletal muscle and adipose tissue mass and quality parameters in patients with liver metastases and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma undergoing Yttrium-90 radioembolization
- PMID: 39838088
- PMCID: PMC11835987
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-025-11349-y
Prognostic value of CT-based skeletal muscle and adipose tissue mass and quality parameters in patients with liver metastases and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma undergoing Yttrium-90 radioembolization
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate baseline patient characteristics associated with the risk of computed tomography (CT)-based sarcopenia and assess whether sarcopenia and other morphometric parameters influence survival outcomes in patients with liver metastases and cholangiocarcinoma after Yttrium-90 radioembolization.
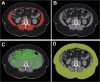
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analyzed 120 cancer patients (mean age, 62 ± 13.3 years, 61 men) who underwent preprocedural CT. Skeletal muscle index (SMI) was measured at the L3 vertebral level to identify sarcopenia. The Cox proportional hazard model was performed to assess the prognostic value of the variables, and Kaplan-Meier analysis with log-rank text was used for overall survival (OS) assessment.
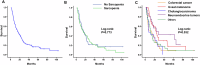
Results: Sarcopenia was diagnosed in 70 patients (58.3%). The multivariate regression analysis demonstrated that male sex, body mass index (BMI), visceral fat radiation attenuation (VFRA), skeletal muscle radiation attenuation (SMRA), and subcutaneous fat radiation attenuation (SFRA) were associated with the incidence of sarcopenia with the odds ratio of 8.81 (95% CI, 2.09-37.1, p = 0.003), 0.64 (95% CI, 0.48-0.85, p = 0.002), 1.23 (95% CI, 1.06-1.42, p = 0.006), 0.79 (95% CI, 0.69-0.91, p = 0.001) and 0.84 (95% CI, 0.76-0.93, p = 0.001), respectively. Age, skeletal muscle index, and tumor subtypes were independent prognostic factors for OS with the hazard ratio of 1.03 (95% CI, 1.01-1.05, p = 0.01), 0.92 (95% CI, 0.86-0.99, p = 0.021) and 2.09 (95% CI, 1.31-3.33 p = 0.002), respectively. In patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, median OS was significantly longer in the non-sarcopenic group than in the sarcopenic patient (25.9 versus 6.5 months, p = 0.029).
Conclusion: Male sex, BMI, VFRA, SMRA, and SFRA were associated with the incidence of sarcopenia. SMI value could be used as a biomarker for OS in patients treated with Yttrium-90 radioembolization.
Key points: Question The prognostic significance of CT-based sarcopenia and other morphometric parameters in patients with liver metastases and cholangiocarcinoma undergoing Yttrium-90 radioembolization remains unclear. Findings A high skeletal muscle index has been identified as an independent protective factor for overall survival in cancer patients treated with Yttrium-90 radioembolization. Clinical relevance The negative impact of CT-based sarcopenia has been confirmed in the context of Yttrium-90 radioembolization. Clinicians should strive to prevent the progression of sarcopenia or maintain skeletal muscle index in perioperative management.
Keywords: Cholangiocarcinoma; Muscle; Prognosis; Sarcopenia; Yttrium-90.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards. Guarantor: The scientific guarantor of this publication is Dr. Duran Rafael. Conflict of interest: R.D.: Consultant: Guerbet, Boston Scientific/BTG, Medtronic, Terumo. Grant: Guerbet, Boston Scientific/BTG, Society of Interventional Oncology, Siemens Healthineers. AntDi: reports honoraria and/or consulting fees from and has served on advisory boards for F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Pharmamar, Incyte, Terumo, Boston Scientific/BTG and AstraZeneca. N.V.: Grant: Boston Scientific, Canon Medical. G.T.: honoraria and/or consulting fees from Boston Scientific. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest. Statistics and biometry: No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Informed consent: Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board. Ethical approval: was obtained from the Institutional Review Board. Study subjects or cohorts overlap: Not applicable. Methodology: Retrospective Observational Performed at one institution
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

