Endocrine and metabolic alterations in response to systemic inflammation and sepsis: a review article
- PMID: 39838305
- PMCID: PMC11752782
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-025-01074-z
Endocrine and metabolic alterations in response to systemic inflammation and sepsis: a review article
Abstract
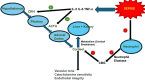
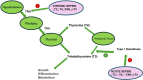
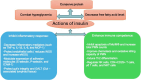
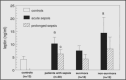
Severe sepsis is cognate with life threatening multi-organ dysfunction. There is a disturbance in endocrine functions with alterations in several hormonal pathways. It has frequently been linked with dysfunction in the hypothalamic pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA). Increased cortisol or cortisolemia is evident throughout the acute phase, along with changes in the hypothalamic pituitary thyroid (HPT) axis, growth hormone-IGF-1 axis, insulin-glucose axis, leptin, catecholamines, renin angiotensin aldosterone axis, ghrelin, glucagon, hypothalamic pituitary gonadal (HGA) axis, and fibroblast growth factor-21. These changes and metabolic alterations constitute the overall response to infection in sepsis. Further research is essential to look into the hormonal changes that occur during sepsis, not only to understand their potential relevance in therapy but also because they may serve as prognostic indicators.
Keywords: Endocrine; Hormones; Inflammation; Metabolism; Sepsis; Septic shock.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors consent for publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Agwunobi AO, Reid C, Maycock P, et al. Insulin resistance and substrate utilization in human endotoxemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(10):3770–8. - PubMed
-
- Alberti C, Brun-Buisson C, Burchardi H, et al. Erratum to: epidemiology of sepsis and infection in ICU patients from an international multicentre cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2002;28(4):525–6. 10.1007/s00134-002-1284-8. - PubMed
-
- Al-Kadi A, El-Daly M, El-Tahawy NFG, Khalifa MMA, Ahmed AF. Angiotensin aldosterone inhibitors improve survival and ameliorate kidney injury induced by sepsis through suppression of inflammation and apoptosis. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2022;36(2):286–95. 10.1111/fcp.12718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

