Initial clinical experience with [177Lu]Lu-PNT2002 radioligand therapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: dosimetry, safety, and efficacy from the lead-in cohort of the SPLASH trial
- PMID: 39839782
- PMCID: PMC11745944
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1483953
Initial clinical experience with [177Lu]Lu-PNT2002 radioligand therapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: dosimetry, safety, and efficacy from the lead-in cohort of the SPLASH trial
Abstract
Introduction: SPLASH (NCT04647526) is a multicenter phase III trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of [177Lu]Lu-PNT2002 radioligand therapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). This study leveraged a lead-in phase to assess tissue dosimetry and evaluate preliminary safety and efficacy, prior to expansion into a randomized phase. Here we report those results.
Methods: Enrolled participants had mCRPC that progressed on one prior androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI), were prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET-positive as determined by a central reader, were chemotherapy-naïve for mCRPC, and had adequate bone marrow and end-organ reserve. Participants received up to 4 cycles of [177Lu]Lu-PNT2002 at 6.8 GBq (± 10%) intravenously per cycle every 8 weeks. Dosimetry (planar + SPECT/CT [n=7]; planar only [n=20]), safety, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) response, objective response rate (ORR), and radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS) per blinded independent central review were assessed.
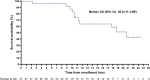
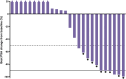
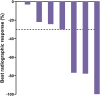
Results: Of 34 individuals screened, 32 underwent PSMA-PET/CT; 27 met all eligibility criteria. Median (range) age was 72 (57-86) years; all participants were enrolled in North America; 40.7% initiated prior ARPI treatment without distant metastases (M0) and 25.9% while hormone sensitive. Nineteen of 27 (70.4%) participants completed all 4 planned cycles. Organs receiving the largest mean (median, range) specific absorbed doses were lacrimal glands at 1.2 (0.9, 0.4-6.7) Gy/GBq (planar only [n=27]), followed by kidneys at 0.73 (0.63, 0.22-1.8) Gy/GBq (planar + SPECT/CT [n=7]; planar only [n=20]). Mean (median, range) tumor specific absorbed dose was 4.3 (2.1, 0.3-33.4) Gy/GBq (approximately 29 Gy/cycle) based on planar + SPECT/CT of 21 lesions in seven participants. [177Lu]Lu-PNT2002 was associated with no treatment-related deaths, few treatment-related grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs), and no discontinuations for unacceptable toxicity. Treatment-related TEAEs occurring in ≥10% of participants included dry mouth (22.2%; all grade 1), fatigue (18.5%; grades 1-2), nausea (18.5%; grades 1-2), and anemia (14.8%; grades 1-3). Median (95% CI) rPFS was 11.5 (9.2-19.1) months, a PSA decline of ≥50% occurred in 42.3% (11/26) of participants, and confirmed ORR for evaluable disease was 50% (5/10).
Conclusion: [177Lu]Lu-PNT2002, administered at 6.8 GBq/cycle for 4 cycles, demonstrated a favorable dosimetry and safety profile, as well as promising preliminary efficacy.
Clinical trial registration: https://clinicaltrials.gov/, identifier NCT04647526.
Keywords: PNT2002; PSMA; castration resistant prostate cancer; dosimetry; radioligand therapy.
Copyright © 2025 Hansen, Probst, Beauregard, Viglianti, Michalski, Tagawa, Sartor, Tutrone, Oz, Courtney, Delpassand, Nordquist, Osman, Chi, Sparks, George, Hawley, Wu, Jensen and Fleshner.
Conflict of interest statement
WW, NG, JJ, and SH are POINT employees. NEF is a former POINT employee. Additional disclosures include grants/contracts: SP AAA/Novartis, J-MB Novartis, KDC Exelixis, Celgene, Myovant, Novartis, Astrazeneca, Surface Oncology, Amgen, Janssen, Clovis Oncology, Harpoon Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, Stemline Therapeutics; NIH grants 2P50CA196516-06A1, 2P30CA142543, and 2UM1-CA186644-06 supporting institution/salary, JM POINT, ST Novartis, Clarity, Ambrx, Gilead, Seagen, Clovis, Merck, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Astellas, Amgen, Janssen, Sanofi, OS AAA, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, In Vitae, Janssen, Lantheus, Merck, Sanofi, POINT, OO American Diabetes Association, Charles Y.C. Pak Foundation, POINT, MedTrace, Clarity, Fusion, Telix, Novartis, KNC Amgen, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, POINT, Roche, NF Janssen, Sanofi, Astellas, Nucleix, Bayer, Progenics, and AH BMS, Pfizer, GSK, Eisai, Janssen, MSD, AstraZeneca, Roche, Boeringer-Ingelheim, Genetech, Marcogenics; consulting fees: SP AAA/Novartis, Bayer, Lantheus, KDC Novartis, ST Sanofi, Astellas, Janssen, Bayer, Abbvie, Seagen, Amgen, Pfizer, Novartis, Clarity, Blue Earth, Aikido, Telix, Convergent, Merck, EMD Serono, Daiichi Sankyo, Ambrx, Regeneron, OS AAA, Amgen, ART BioScience, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Clarity Pharmaceuticals, EMD Serono, Fusion, Isotopen Technologien, Janssen, MacroGenics, Novartis, Pfizer, POINT, Ratio, Sanofi, Telix, TeneoBio, KNC Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, BMS, Janssen Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, POINT, Roche, RS POINT, Novartis, NF Amgen, Sanofi, Janssen, Abbvie, Astellas, Ferring, Bayer, and AH MSD, Pfizer, Bayer; payment/honoraria: J-MB IPSEN, Novartis, KDC Targeted Oncology, RT Myovant, MMO Lantheus, OO Society of Nuclear Medicine, Taiwan Annual Meeting 2022, KNC Astellas, Janssen, and ARH MSD, Bayer; receipt of equipment, materials, drugs, medical writing, gifts, or other services: SP Lantheus and KNC Janssen; travel support: OS Bayer, Lantheus, Sanofi and NF POINT; DSMB/Advisory Board participation: J-MB Novartis, OS Pfizer, Merck, Janssen, AAA, Novartis, AstraZeneca, and RS Pfizer/Astellas, Novartis; stock/stock options: KDC former Regeneron ownership by spouse, ST Aikido, Convergent, OS AbbVie, Cardinal Health, Clarity, Convergent, Eli Lilly, Fusion, Abbot, Ratio, United Health Group, Telix, RS Novartis, and WW, SH, NG, JJ, and NF POINT; former; payment for expert testimony: OS Sanofi; planned patent for a PET hepatobiliary agent: OO; leadership positions of CMO for POINT NF; former and Verity NF; former. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision. The authors declare that this study received funding from POINT. POINT Biopharma provided funding for SPLASH to the institutions of SP, J-MB, BV, KDC, JM, ST, OS, RT, OO, ED, LN, MO, KNC, and AH. POINT Biopharma and Lantheus provided medical writing support and article processing charges on behalf of all authors.
Figures

References
-
- Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Laversanne M, Colombet M, Mery L, et al. . Global cancer observatory: cancer today (2020). Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available online at: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today (Accessed October 1, 2023).
-
- Taxotere [Prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Sanofi-Aventis U.S. LLC; (2013).
-
- Jevtana [Prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Sanofi-Aventis U.S. LLC; (2010).
-
- Provenge [Prescribing information]. Seal Beach, CA: Dendreon Corp; (2010).
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

