C-X-C chemokine receptor type 5+CD8+ T cells as immune regulators in hepatitis Be antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B under interferon-alpha treatment
- PMID: 39839901
- PMCID: PMC11684170
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i3.99833
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 5+CD8+ T cells as immune regulators in hepatitis Be antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B under interferon-alpha treatment
Abstract
Background: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 5 (CXCR5)+CD8+ T cells represent a unique immune subset with dual roles, functioning as cytotoxic cells in persistent viral infections while promoting B cell responses. Despite their importance, the specific role of CXCR5+CD8+ T cells in chronic hepatitis B (CHB), particularly during interferon-alpha (IFN-α) treatment, is not fully understood. This study aims to elucidate the relationship between CXCR5+CD8+ T cells and sustained serologic response (SR) in patients undergoing 48 weeks of pegylated IFN-α (peg-IFN-α) treatment for CHB.
Aim: To elucidate the relationship between CXCR5+CD8+ T cells and sustained SR in patients undergoing 48 weeks of peg-IFN-α treatment for CHB.
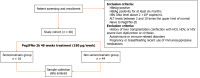
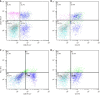
Methods: This study enrolled 60 patients with hepatitis Be antigen (HBeAg)-positive CHB undergoing 48 weeks of peg-IFN-α treatment. Participants were assessed for eligibility based on criteria such as persistent HBsAg-positive status for at least six months, HBeAb-negative, hepatitis B virus DNA levels exceeding 2 × 104 copies/mL, and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels between 2 and 10 times the upper limit of normal. Blood samples were collected at baseline and at weeks 12, 24, 48, and a 24-week treatment-free follow-up (week 72) to measure serum interleukin (IL)-21 concentration via ELISA and to analyze CXCR5 and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression on CD8+ T cells by flow cytometry, CXCR5 is a chemokine receptor that directs immune cells to specific tissues, while PD-L1 is a protein that regulates immune responses by inhibiting T cell activity.
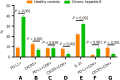
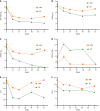
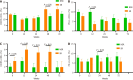
Results: Patients with CHB exhibited significantly lower levels of circulating CXCR5+CD8+ T cells compared to healthy controls (P < 0.01). Notably, CXCR5+CD8+ T cells were prominently expressed in patients who achieved sustained SR compared to non-SR (NSR). A significant correlation was observed between CXCR5 and PD-L1 expression (r = -0.189, P = 0.002). However, there was no significant correlation between serum IL-21 levels and CXCR5+CD8+ lymphocytes (r = -0.03, P = 0.625) or serum ALT levels (r = 0.026, P = 0.678).
Conclusion: The enhanced expression of CXCR5+CD8+ T cells in patients achieving HBeAg seroconversion during IFN-α treatment suggests that these cells play a crucial role in antiviral immune responses against hepatitis B. This study highlights the potential of CXCR5+CD8+ T cells as immune regulators in CHB, which may inform future therapeutic strategies to optimize antiviral treatments.
Keywords: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 5; Chronic hepatitis B; Interleukin -21; Pegylated interferon-alpha; Programmed death-ligand 1.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
[Effects of PEG-IFN-α treatment on the expression of CD+161 and PD-1 in CD8+ T cells of patients with chronic hepatitis B].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2025 Jun 20;33(6):570-576. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20240921-00501. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40660987 Chinese.
-
VIR-2218 (elebsiran) plus pegylated interferon-alfa-2a in participants with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a phase 2 study.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Dec;9(12):1121-1132. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(24)00237-1. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39389081 Clinical Trial.
-
Altered LY6E and TRIM6 expression in PBMCs correlated with HBsAg clearance and response to Peg-IFN-α treatment in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients.Virol J. 2025 Mar 15;22(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02689-8. Virol J. 2025. PMID: 40089754 Free PMC article.
-
Pegylated interferon alpha-2a and -2b in combination with ribavirin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2004 Oct;8(39):iii-iv, 1-125. doi: 10.3310/hta8390. Health Technol Assess. 2004. PMID: 15461877
References
-
- Xun Z, Lin J, Yu Q, Liu C, Huang J, Shang H, Guo J, Ye Y, Wu W, Zeng Y, Wu S, Xu S, Chen T, Chen J, Ou Q. Taurocholic acid inhibits the response to interferon-α therapy in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B by impairing CD8+ T and NK cell function. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18:461–471. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Tang L, Guo L, Chen C, Gu S, Zhou Y, Ye G, Li X, Wang W, Liao X, Wang Y, Peng X, Liu G, Zhang X, Sun J, Peng J, Hou J. CXCL13-mediated recruitment of intrahepatic CXCR5+CD8+ T cells favors viral control in chronic HBV infection. J Hepatol. 2020;72:420–430. - PubMed
-
- Chu F, Li HS, Liu X, Cao J, Ma W, Ma Y, Weng J, Zhu Z, Cheng X, Wang Z, Liu J, Jiang ZY, Luong AU, Peng W, Wang J, Balakrishnan K, Yee C, Dong C, Davis RE, Watowich SS, Neelapu SS. CXCR5+CD8+ T cells are a distinct functional subset with an antitumor activity. Leukemia. 2019;33:2640–2653. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

