Innovative bioinks for 3D bioprinting: Exploring technological potential and regulatory challenges
- PMID: 39839985
- PMCID: PMC11748162
- DOI: 10.1177/20417314241308022
Innovative bioinks for 3D bioprinting: Exploring technological potential and regulatory challenges
Abstract
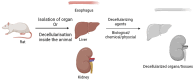
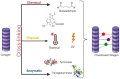
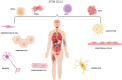
The field of three dimensional (3D) bioprinting has witnessed significant advancements, with bioinks playing a crucial role in enabling the fabrication of complex tissue constructs. This review explores the innovative bioinks that are currently shaping the future of 3D bioprinting, focusing on their composition, functionality, and potential for tissue engineering, drug delivery, and regenerative medicine. The development of bioinks, incorporating natural and synthetic materials, offers unprecedented opportunities for personalized medicine. However, the rapid technological progress raises regulatory challenges regarding safety, standardization, and long-term biocompatibility. This paper addresses these challenges, examining the current regulatory frameworks and the need for updated guidelines to ensure patient safety and product efficacy. By highlighting both the technological potential and regulatory hurdles, this review offers a comprehensive overview of the future landscape of bioinks in bioprinting, emphasizing the necessity for cross-disciplinary collaboration between scientists, clinicians, and regulatory bodies to achieve successful clinical applications.
Keywords: 3D bioprinting; bioinks; biomedical application; crosslinking.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Mabrouk M, Beherei HH, Das DB. Recent progress in the fabrication techniques of 3D scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C 2020; 110: 110716. - PubMed
-
- Vigani B, Ianev D, Adami M, et al.. Porous functionally graded scaffold prepared by a single-step freeze-drying process. A bioinspired approach for wound care. Int J Pharm 2024; 656: 124119. - PubMed
-
- Azarsa S, Pezeshki-Modaress M, Yazdian F, et al.. Nanofiber/hydrogel composite scaffolds based on alginate sulfate and extracellular matrix for cartilage tissue engineering applications. Process Biochem 2024; 136: 60–71.
-
- Ng WL, Chua CK, Shen YF. Print me an organ! Why we are not there yet. Prog Polym Sci 2019; 97: 101145.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

