LC-MS/MS assisted pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution study of ropivacaine and 3-OH-ropivacaine on rats after plane block anesthesia
- PMID: 39840090
- PMCID: PMC11746028
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1494646
LC-MS/MS assisted pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution study of ropivacaine and 3-OH-ropivacaine on rats after plane block anesthesia
Abstract
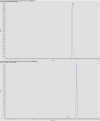
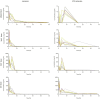
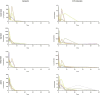
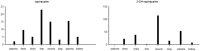
Knowledge of drug pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution is precious for ensuring patient safety and optimizing treatments. The varied use of local anesthetics, as well as the fact that anesthetics can sometimes have low therapeutic indices and numerous adverse drug reactions, makes any novel pharmacokinetics information valuable. The present manuscript describes a pharmacokinetic study of ropivacaine carried out after plane block anesthesia on an animal model, using high sensitivity, accurate, and precise LC-MS/MS bioanalysis. Both plasmatic concentrations and tissue distribution of ropivacaine and its primary active metabolite were determined. The results showed a tissue affinity of the anesthetics, a clearance of ropivacaine mainly by hepatic metabolism, and the final, mainly renal excretion of the hydroxylated metabolite. While the results cannot simply and directly be transposed to human pharmacokinetics, they offer a valuable basis for future studies and can contribute to a better understanding of the bioavailability and toxicology of the widely used modern anesthetic.
Keywords: HPLC; LC-MS/MS; pharmacokinetics; rats; ropivacaine.
Copyright © 2025 Butiulca, Farczadi, Imre, Vari, Vlase, Cordos, Azamfirei and Lazar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ekstrom G., Gunnarsson U. B. (1996). Ropivacaine, a new amide-type local anesthetic agent, is metabolized by cytochromes P450 1A and 3A in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 24, 955–961. - PubMed
-
- EMA (2011). Guideline on bioanalytical method validation. (EMEA/CHMP/EWP/192217/2009). European Medicines Agency EMA (Accessed August 2024).
-
- FDA (2018). Bioanalytical method validation guidance for industry. United Stated: FDA.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

