Uvaol attenuates TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human alveolar epithelial cells by modulating expression and membrane localization of β-catenin
- PMID: 39840107
- PMCID: PMC11747490
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1504556
Uvaol attenuates TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human alveolar epithelial cells by modulating expression and membrane localization of β-catenin
Abstract
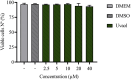
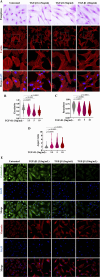
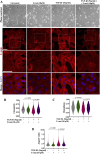
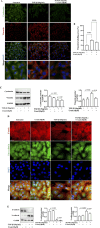
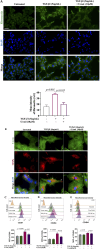
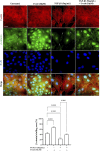
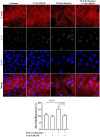
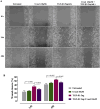
The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a biological process in which epithelial cells change into mesenchymal cells with fibroblast-like characteristics. EMT plays a crucial role in the progression of fibrosis. Classical inducers associated with the maintenance of EMT, such as TGF-β1, have become targets of several anti-EMT therapeutic strategies. Natural products from the pentacyclic triterpene class have emerged as promising elements in inhibiting EMT. Uvaol is a pentacyclic triterpene found in olive trees (Olea europaea L.) known for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiproliferative properties. Yet, its effect on the TGF-β1-induced EMT in alveolar epithelial cells is unknown. The present study aimed to investigate the impact of uvaol upon TGF-β1-induced EMT in a cultured A549 human alveolar epithelial cell line, a classic in vitro model for studies of EMT. Changes in cell shape were measured using phase-contrast and confocal microscopy, whereas protein expression levels were measured using immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, and Western blotting. We also performed wound scratch experiments to explore its effects on cell migration. Uvaol had no significant cytotoxic effects on A549 cells. By contrast, the changes in the cell morphology consistent with TGF-β1-induced EMT were largely suppressed by treatment with uvaol. In addition, increased contents of mesenchymal markers, namely, vimentin, N-cadherin, and fibronectin in TGF-β1-induced A549 cells, were downregulated by uvaol treatment. Furthermore, the TGF-β1-induced migration of A549 cells was significantly suppressed by uvaol. Mechanistically, uvaol prevented the nuclear translocation of β-catenin and reduced the TGF-β1-induced levels of ZEB1 in A549 cells. These results provide compelling evidence that uvaol inhibits EMT by regulating proteins related to the mesenchymal profile in human alveolar epithelial cells, likely by modulating β-catenin and ZEB1 levels.
Keywords: TGF-β1; cell migration; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; uvaol; β-catenin.
Copyright © 2025 Patrícia Gonçalves Tenório, Xavier, Silveira Wagner, Moreira Bagri, Alves Ferreira, Galvani, Mermelstein, Bonomo, Savino and Barreto.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Allouche Y., Warleta F., Campos M., Sánchez-Quesada C., Uceda M., Beltrán G., et al. (2011). Antioxidant, antiproliferative, and pro-apoptotic capacities of pentacyclic triterpenes found in the skin of olives on MCF-7 human breast cancer cells and their effects on DNA damage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 59 (1), 121–130. 10.1021/JF102319Y - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonel-Pérez G. C., Pérez-Jiménez A., Gris-Cárdenas I., Parra-Pérez A. M., Lupiáñez J. A., Reyes-Zurita F. J., et al. (2020). Antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effect of uvaol in human hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells by affecting G0/G1 cell cycle arrest, ROS production and AKT/PI3K signaling pathway. Mol. Basel, Switz. 25 (18), 4254. 10.3390/MOLECULES25184254 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

