Polydatin retards the progression of osteoarthritis by maintaining bone metabolicbalance and inhibiting macrophage polarization
- PMID: 39840130
- PMCID: PMC11747576
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1514483
Polydatin retards the progression of osteoarthritis by maintaining bone metabolicbalance and inhibiting macrophage polarization
Abstract
Background: Polydatin (PD), also known as tiger cane glycoside, is a natural compound extracted from the Japanese knotweed plant, which is often referred to as white resveratrol. It exhibits anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic effects in the treatment of various diseases. However, the potential molecular mechanisms of PD in osteoarthritis have not been clearly elucidated.
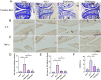
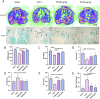
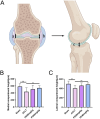
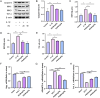
Methods: Anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT) surgery was performed to establish an osteoarthritis animal model. Female mice at the age of 12 weeks were intraperitoneally injected with different concentrations of PD (20 and 40 mg/kg). In vitro models were established by isolating mouse articular chondrocytes, which were subsequently treated with lipopolysaccharide or IL-1β for 24 h for subsequent experiments. In addition, different concentrations of PD were administered for 12 h. Morphological changes were observed by toluidine blue staining, joint bone metabolism changes were observed by tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase staining, immunohistochemistry was used to observe the expression levels of inflammatory factors and extracellular matrix. MicroCT analysis was conducted to assess changes in the microstructure of subchondral bone trabeculae, and Western blot was performed to measure the expression of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling pathway and markers of M1 polarization in macrophages.
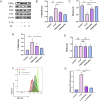
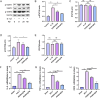
Results: PD significantly delays the progression of osteoarthritis induced by ACLT, effectively inhibits IL-1β-induced joint inflammation, bone metabolic remodeling and extracellular matrix degradation. In addition, paeoniflorin markedly suppresses the transmission of the NF-κB signaling pathway and reverses M1 polarization in macrophages induced by IL-1β.
Conclusion: Taken together, PD might be a potential therapeutic agent for the prevention and treatment of osteoarthritis.
Keywords: NF-κB; Polydatin; cartilage; extracellular matrix; osteoarthritis.
Copyright © 2025 Sun, Nan, Wang, Pan, Ji, Guo, Zhao, Li, Guo, Lin, Jin, Zhang, Liu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

