Predicting the location of coordinated metal ion-ligand binding sites using geometry-aware graph neural networks
- PMID: 39840139
- PMCID: PMC11750443
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.12.016
Predicting the location of coordinated metal ion-ligand binding sites using geometry-aware graph neural networks
Abstract
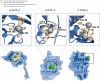
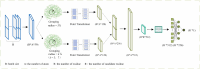
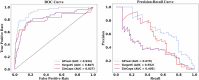
More than 50 % of proteins bind to metal ions. Interactions between metal ions and proteins, especially coordinated interactions, are essential for biological functions, such as maintaining protein structure and signal transport. Physiological metal-ion binding prediction is pivotal for both elucidating the biological functions of proteins and for the design of new drugs. However, accurately predicting these interactions remains challenging. In this study, we proposed GPred, a novel structure-based method that transforms the 3-dimensional structure of a protein into a point cloud representation and then designs a geometry-aware graph neural network to learn the local structural properties of each amino acid residue under specific ligand-binding supervision. We trained our model to predict the location of coordinated binding sites for five essential metal ions: Zn2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Mn2+, and Fe2+. We further demonstrated the versatility of GPred by applying transfer learning to predict the binding sites of 2 heavy metal ions, that is, cadmium (Cd2+) and mercury (Hg2+). We achieved greater than 19.62 %, 14.32 %, 36.62 %, and 40.69 % improvement in the area under the precision-recall curve (AUPR) of Zn2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Mn2+, and Fe2+, respectively, when compared with 6 current accessible state-of-the-art sequence-based or structure-based tools. We also validated the proposed approach on protein structures predicted by AlphaFold2, and its performance was similar to experimental protein structures. In both cases, achieving a low false discovery rate for proteins without annotated ion-binding sites was demonstrated. © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Keywords: Binding sites; Graph neural network; Metal ions; Point cloud; Protein structures.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Raff M., Alberts B., Lewis J., et al. Mol Biol Cell 4th Ed. 2002
-
- Von Hippel P.H., Schleich T. Ion effects on the solution structure of biological macromolecules. Acc Chem Res. 1969;2(9):257–265.
-
- Urnov F.D., Rebar E.J., Holmes M.C., et al. Genome editing with engineered zinc finger nucleases. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11(9):636–646. - PubMed
-
- Ram B.P., Munjal D.D., Fraser I.H. Galactosyltransferases: physical, chemical, and biological aspect. Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;17(3):257–311. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
