Percutaneous ballon compression, a better choice for primary trigeminal neuralgia compared to microvascular decompression?
- PMID: 39840265
- PMCID: PMC11747207
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1517064
Percutaneous ballon compression, a better choice for primary trigeminal neuralgia compared to microvascular decompression?
Abstract
Objective: Demonstrate the superiority of percutaneous balloon compression (PBC) in the treatment of primary trigeminal neuralgia (PTN) compared to trigeminal microvascular decompression (MVD).
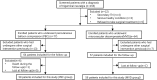
Methods: Clinical data, including immediate, short-term, and long-term pain relief, complications, duration of the operation, and postoperative hospital stay, were retrospectively analyzed for 114 patients diagnosed with PTN who were treated with either PBC or MVD between January 2018 and December 2021.
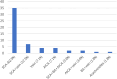
Results: There were no statistically significant differences observed in the pain relief rates between the two surgical methods at 24 h postoperatively (MVD: 91.07%, PBC: 96.55%), at 6 months postoperatively (MVD: 87.5%, PBC: 94.8%), at 1 year postoperatively (MVD: 83.90%, PBC: 94.80%), and at 2 years postoperatively (MVD: 78.60%, PBC: 72.40%). However, the incidence of meningitis following MVD was significantly higher than that following PBC (P < 0.005). Additionally, both the duration of the operation and the length of the postoperative hospital stay in the MVD group were longer than those in the PBC group (P < 0.005).
Conclusion: PBC demonstrates efficacy comparable to MVD while offering a simpler procedure, improved safety, and a shorter postoperative hospital stay. Therefore, it may serve as a viable alternative to MVD and could become the preferred surgical approach for treating PTN in the future.
Keywords: efficacy & safety; operation duration; percutaneous balloon compression (PBC); postoperative hospital stay; primary trigeminal neuralgia (PTN); trigeminal microvascular decompression (MVD).
© 2025 Shi, Liu, Peng and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of microvascular decompression and percutaneous balloon compression efficacy in patients with V2 idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 15;15:1406602. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1406602. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39474365 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous balloon compression (PBC) of trigeminal ganglion for recurrent trigeminal neuralgia after microvascular decompression (MVD).Ir J Med Sci. 2015 Dec;184(4):745-51. doi: 10.1007/s11845-014-1163-7. Epub 2014 Jun 21. Ir J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 24951087
-
Comparison of percutaneous balloon compression and microvascular decompression in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia.Pak J Med Sci. 2023 Sep-Oct;39(5):1451-1455. doi: 10.12669/pjms.39.5.8049. Pak J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37680844 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of microvascular decompression versus percutaneous balloon compression in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Palliat Med. 2022 Apr;11(4):1391-1400. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-3901. Ann Palliat Med. 2022. PMID: 35523747
-
The Focus and New Progress of Percutaneous Balloon Compression for the Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia.J Pain Res. 2022 Sep 29;15:3059-3068. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S374433. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 36199499 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources