Detection of clinically relevant variants in the TP53 gene below 10% allelic frequency: A multicenter study by ERIC, the European Research Initiative on CLL
- PMID: 39840379
- PMCID: PMC11746920
- DOI: 10.1002/hem3.70065
Detection of clinically relevant variants in the TP53 gene below 10% allelic frequency: A multicenter study by ERIC, the European Research Initiative on CLL
Abstract
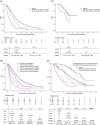
In chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the reliability of next-generation sequencing (NGS) to detect TP53 variants ≤10% allelic frequency (low-VAF) is debated. We tested the ability to detect 23 such variants in 41 different laboratories using their NGS method of choice. The sensitivity was 85.6%, 94.5%, and 94.8% at 1%, 2%, and 3% VAF cut-off, respectively. While only one false positive (FP) result was reported at >2% VAF, it was more challenging to distinguish true variants <2% VAF from background noise (37 FPs reported by 9 laboratories). The impact of low-VAF variants on time-to-second-treatment (TTST) and overall survival (OS) was investigated in a series of 1092 patients. Among patients not treated with targeted agents, patients with low-VAF TP53 variants had shorter TTST and OS versus wt-TP53 patients, and the relative risk of second-line treatment or death increased continuously with increasing VAF. Targeted therapy in ≥2 line diminished the difference in OS between patients with low-VAF TP53 variants and wt-TP53 patients, while patients with high-VAF TP53 variants had inferior OS compared to wild type-TP53 cases. Altogether, NGS-based approaches are technically capable of detecting low-VAF variants. No strict threshold can be suggested from a technical standpoint, laboratories reporting TP53 mutations should participate in a standardized validation set-up. Finally, whereas low-VAF variants affected outcomes in patients receiving chemoimmunotherapy, their impact on those treated with novel therapies remains undetermined. Our results pave the way for the harmonized and accurate TP53 assessment, which is indispensable for elucidating the role of TP53 mutations in targeted treatment.
© 2025 The Author(s). HemaSphere published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Hematology Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Bárbara Tazón‐Vega: Honoraria: Bristol Meyer Squibb. Beatriz Bellosillo: Advisory board honoraria, research support, travel support, speaker fees: Astra‐Zeneca, BMS, Janssen, Merck‐Serono, Novartis, Pfizer, Hoffman‐La Roche, ThermoFisher. Christian Brieghel: Travel grant: Octapharma. Carsten U. Niemann: Research funding and/or consultancy fees: Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Beigene, Janssen, Genmab, Lilly, MSD, CSL Behring, Takeda, Octapharma. Davide Rossi: Honoraria: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, BMS, Janssen, Lilly. Research grants: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Janssen. Travel grants: AstraZeneca, Janssen. Eugen Tausch: Honoraria and research support: Abbvie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Janssen, Hoffmann‐La Roche; Research support from Abbvie, Roche, Gilead. Frédéric Davi: Honoraria: Janssen, AstraZeneca. Kostas Stamatopoulos: Research funding, honoraria and/or consultancy fees: Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Lilly, Roche. Lydia Scarfo: Consultancy: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Janssen, Lilly; Speaker Bureau: Octapharma. Miguel Alcoceba: Honoraria and travel grants: Janssen, AstraZeneca. Martin Andres: Consultancy, Honoraria, and travel support: AstraZeneca, Novartis, Roche, Janssen‐Cilag. Maria Gomes da Silva: Consultancy and Research Funding: Janssen Cilag, AstaZeneca, Abbvie, Roche, Takeda. Pau Abrisqueta: Consultancy and Honoraria: Janssen, Abbvie, Roche, BMS, AstraZeneca, Genmab. Panagiotis Baliakas: Honoraria: Abbvie, Gilead, Janssen. Research funding: Gilead. Paolo Ghia: Honoraria: AbbVie, Astrazeneca, BeiGene, BMS, Galapagos, Janssen, Lilly/Loxo Oncology, MSD, Roche. Research funding: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BMS, Janssen. Richard Rosenquist: Honoraria: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Illumina, Roche. Renata Walewska: Travel support: AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Beigene. Sylwia Czekalska: Honoraria: AstraZeneca. Funding: Janssen, AstraZeneca. Stephan Stilgenbauer: Advisory board honoraria, research support, travel support, speaker fees: AbbVie, Acerta, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, BMS, Celgene, Gilead, GSK, Hoffmann‐La Roche, Infinity, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Sunesis, Verastem. Tiina Kahre: Honoraria: AstraZeneca. Tomasz Stokłosa: Honoraria and Research Funding: Janssen, AstraZeneca. The remaining authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Döhner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, et al. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(26):1910‐1916. - PubMed
-
- Sharman JP, Egyed M, Jurczak W, et al. Efficacy and safety in a 4‐year follow‐up of the ELEVATE‐TN study comparing acalabrutinib with or without obinutuzumab versus obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil in treatment‐naïve chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2022;36(4):1171‐1175. 10.1038/s41375-021-01485-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
