A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Prevalence of Aflatoxin M1 in Dairy Products in Selected Middle East Countries
- PMID: 39840829
- PMCID: PMC11752159
- DOI: 10.1002/vms3.70204
A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Prevalence of Aflatoxin M1 in Dairy Products in Selected Middle East Countries
Abstract
Background: Human consumption of dairy products contaminated with aflatoxin (AF) M1 can lead to severe health issues. This AF's significance and impact on health necessitate a thorough investigation of its prevalence in dairy products.
Objectives: This study aims to determine the prevalence of AFM1 in dairy products through a systematic review and meta-analysis, focusing on data from Middle Eastern countries.
Methods: We identified relevant studies through electronic database searches (PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science) up to August 2023. We employed a random-effects model to derive an overall estimate and used 95% confidence intervals to determine pooled prevalence rates.
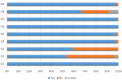
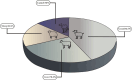
Results: The meta-analysis included 193 studies encompassing 297,530 samples of dairy products. The results showed that AFM1 contaminated 87% of dairy products. The following is a ranking of countries based on the prevalence of AFM1 in their dairy products: Iran > Jordan > Turkey > Kuwait > Lebanon > Syria > Egypt > Cyprus > the United Arab Emirates. The current meta-analysis indicated that Middle Eastern countries exhibited a high prevalence of AFM1 in dairy products. The prevalence rates for AFM1 in various dairy products were as follows: milk (87%), yogurt (68.9%), cheese (63.6%), kashk (62.9%), doogh (55.6%) and ice cream (54%). Pasteurized milk (99.5%), ultra-high temperature (91.3%), raw milk (73%) and traditional milk (51%), among other milk types, had the highest contamination rates.
Conclusion: The study reveals a high prevalence of AFM1 in dairy products, particularly in Middle Eastern countries. Given the critical importance of milk and dairy products in the diet, special measures are needed to safeguard their quality and protect consumers from AF contamination.
Keywords: aflatoxin M1; cheese; meta‐analysis; milk; mycotoxins; prevalence.
© 2025 The Author(s). Veterinary Medicine and Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prevalence and concentration of aflatoxin M1 in milk and dairy products: an umbrella review of meta-analyses.Int Health. 2025 Jul 1;17(4):403-415. doi: 10.1093/inthealth/ihaf002. Int Health. 2025. PMID: 39850982 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of aflatoxin M1 in milk of Middle East region: A systematic review, meta-analysis and probabilistic health risk assessment.Food Chem Toxicol. 2018 Aug;118:653-666. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.06.016. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29902498
-
The prevalence of aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) in conventional and industrial dairy products (yogurt, cheese, kashk and dough) of Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Rev Environ Health. 2021 May 14;37(1):123-135. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2021-0028. Print 2022 Mar 28. Rev Environ Health. 2021. PMID: 33984875
-
Review, meta-analysis and carcinogenic risk assessment of aflatoxin M1 in different types of milks in Iran.Rev Environ Health. 2022 Jun 24;38(3):511-518. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2022-0050. Print 2023 Sep 26. Rev Environ Health. 2022. PMID: 35749130
-
The occurrence and human health risk assessment of aflatoxin M1 in ice cream collected from Iranian market.Mycotoxin Res. 2025 Aug;41(3):405-414. doi: 10.1007/s12550-025-00591-4. Epub 2025 May 7. Mycotoxin Res. 2025. PMID: 40332654
References
-
- Abyaneh, H. K. , Bahonar A., Noori N., Yazdanpanah H., and AliAbadi M. H. S.. 2020. “The Overall and Variations of Aflatoxin M1 Contamination of Milk in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis Study.” Food Chemistry 310: 125848. - PubMed
-
- Acaroz, U. 2019. “Assessment of Aflatoxin M1 Levels in Tulum and White Cheeses in Afyonkarahisar, Turkey.” Fresenius Environ Bullet 28: 8663–8668.
-
- Adam, A. , Aly S., Sayed R., and Saad M.. 2021. “Occurrence of Aflatoxin M1 in Cheese and Yoghurt Marketed at El‐Fayoum Province, Egypt.” International Journal of Dairy Science 16: 146–152.
-
- Ahmadi, E. 2020. “Potential Public Health Risk Due to Consumption of Contaminated Bovine Milk With Aflatoxin M1 and Coxiella burnetii in the West of Iran.” International Journal of Dairy Technology 73: 479–485.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

