Optimizing genome editing efficiency in Streptomyces fradiae via a CRISPR/Cas9n-mediated editing system
- PMID: 39840981
- PMCID: PMC11837490
- DOI: 10.1128/aem.01953-24
Optimizing genome editing efficiency in Streptomyces fradiae via a CRISPR/Cas9n-mediated editing system
Abstract
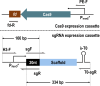
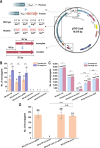
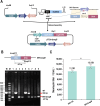
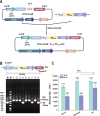
Streptomyces fradiae is an important bioresource to produce various antibacterial natural products, however, the time-consuming and labor-intensive genome editing toolkits hindered the construction and application of engineered strains, and this study aimed to establish an efficient CRISPR/Cas9n genome editing system in S. fradiae. Initially, the CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing tool was employed to replace those awkward genome editing tools that relied on homologous recombination, while the off-target Cas9 exhibited high toxicity to S. fradiae Sf01. Therefore, the nickase mutation D10A, high-fidelity mutations including N497A, R661A, Q695A, and Q926A, and thiostrepton-induced promotor PtipA were incorporated into the Cas9 expression cassette, which reduced its toxicity. The deletion of single gene neoI and long fragment sequence (13.3 kb) were achieved with efficiencies of 77.8% and 44%, respectively. Additionally, the established tool was applied to facilitate the rapid deletion of nagB, replacement of Pfrr with PermE*, and integration of exogenous vgbS, with respective efficiencies of 77.8%, 100%, and 67.8%, and all of the above modification strategies benefited neomycin synthesis in S. fradiae. Taken together, this research established an efficient CRISPR/Cas9n-mediated genome editing toolkit in S. fradiae, paving the way for developing high-performance neomycin-producing strains and facilitating the genetic modification of Streptomyces.IMPORTANCEThis study describes the development and application of a genome editing system mediated by CRISPR/Cas9n in Streptomyces fradiae for the first time, which overcomes the challenges associated with genome editing caused by high GC content (74.5%) coupling with complex genome structure, and reduces the negative impact of "off-target effect." Our work not only provides a facile editing tool for constructing S. fradiae strains of high-yield neomycin but also offers the technical guidance for the design of a CRISPR/Cas9n mediated genome editing tool in those creatures with high GC content genomes.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9D10A; Streptomyces fradiae; metabolic engineering; neomycin; single strand breaks repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development of an Efficient Genome Editing Tool in Bacillus licheniformis Using CRISPR-Cas9 Nickase.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Mar 1;84(6):e02608-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02608-17. Print 2018 Mar 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29330178 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a CRISPR/Cas9D10A Nickase (nCas9)-Mediated Genome Editing Tool in Streptomyces.ACS Synth Biol. 2023 Oct 20;12(10):3114-3123. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00466. Epub 2023 Sep 18. ACS Synth Biol. 2023. PMID: 37722085
-
CRISPR-Cpf1-Assisted Multiplex Genome Editing and Transcriptional Repression in Streptomyces.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Aug 31;84(18):e00827-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00827-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29980561 Free PMC article.
-
Editing streptomycete genomes in the CRISPR/Cas9 age.Nat Prod Rep. 2019 Sep 18;36(9):1237-1248. doi: 10.1039/c8np00081f. Nat Prod Rep. 2019. PMID: 30680376 Review.
-
Challenges of in vitro genome editing with CRISPR/Cas9 and possible solutions: A review.Gene. 2020 Aug 30;753:144813. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144813. Epub 2020 May 26. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32470504 Review.
References
-
- Vatlin AA, Bekker OB, Lysenkova LN, Shchekotikhin AE, Danilenko VN. 2020. Bioinformatics analysis of genes of Streptomyces xinghaiensis (fradiae) ATCC 19609 with A focus on mutations conferring resistance to oligomycin A and its derivatives. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 22:47–53. doi:10.1016/j.jgar.2020.01.026 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

