Intercellular mRNA transfer alters the human pluripotent stem cell state
- PMID: 39841146
- PMCID: PMC11789055
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2413351122
Intercellular mRNA transfer alters the human pluripotent stem cell state
Abstract
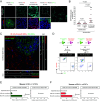
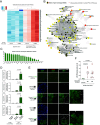
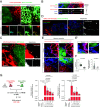
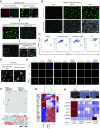
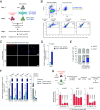
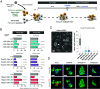
Intercellular transmission of messenger RNA (mRNA) is being explored in mammalian species using immortal cell lines. Here, we uncover an intercellular mRNA transfer phenomenon that allows for the adaptation and reprogramming of human primed pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs). This process is induced by the direct cell contact-mediated coculture with mouse embryonic stem cells under the condition impermissible for primed hPSC culture. Mouse-derived mRNA contents are transmitted into adapted hPSCs only in the coculture. Transfer-specific mRNA analysis shows the enrichment for divergent biological pathways involving transcription/translational machinery and stress-coping mechanisms, wherein such transfer is diminished when direct cell contacts are lost. After 5 d of coculture with mouse embryonic stem cells, surface marker analysis and global gene profiling confirmed that mRNA transfer-prone hPSC efficiently gains a naïve-like state. Furthermore, transfer-specific knockdown experiments targeting mouse-specific transcription factor-coding mRNAs in hPSC show that mouse-derived Tfcp2l1, Tfap2c, and Klf4 are indispensable for human naïve-like conversion. Thus, interspecies mRNA transfer triggers cellular reprogramming in mammalian cells. Our results support that episodic mRNA transfer can occur in cell cooperative and competitive processes, which provides a fresh perspective on understanding the roles of mRNA mobility for intra- and interspecies cellular communications.
Keywords: cell–cell communication; mRNA transfer; pluripotency; reprogramming.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Update of
-
Inter-cellular mRNA Transfer Alters Human Pluripotent Stem Cell State.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 27:2024.06.27.600209. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.27.600209. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jan 28;122(4):e2413351122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2413351122. PMID: 38979277 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Valadi H., et al. , Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 654–659 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Jiang H., Li Z., Li X., Xia J., Intercellular transfer of messenger RNAs in multiorgan tumorigenesis by tumor cell-derived exosomes. Mol. Med. Rep. 11, 4657–4663 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

