A Snapshot of United States Sarcoidosis Patients and their Perceived Disease Impact: Results of the Sarcoidosis Research Institute Survey
- PMID: 39841245
- PMCID: PMC11754370
- DOI: 10.1007/s00408-024-00761-8
A Snapshot of United States Sarcoidosis Patients and their Perceived Disease Impact: Results of the Sarcoidosis Research Institute Survey
Abstract
Purpose: The priorities and concerns of sarcoidosis patients in the United States (US) have not been well-described.
Methods: A survey constructed by sarcoidosis patients and doctors was administered to US sarcoidosis patients. The survey queried patients concerning their demographics, disease state, disease impact on health and well-being, health care priorities and impressions of sarcoidosis care. Respondents were solicited via social media and networking with sarcoidosis clinicians.
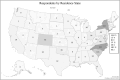
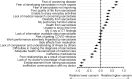
Results: 1018 US sarcoidosis patients completed this survey. 65% were female, 63% White, 34% Black, and 87% > 45 years old. The most common organs involved were the lungs 87%, skin 30%, heart 25%, and eyes 25%. Household income was < $50 K in 31% and > $150 K in 14% of patients. There was a fairly even split between those living in urban (29%), suburban (42%), and rural (29%) environments. The patients'greatest concerns were fear of worsening disease, fear of sarcoidosis developing in more organs, and fear of sarcoidosis not improving. These were closely followed by concerns about poor health-related quality of life (HRQoL), inability to enjoy everyday activities, lack of medical research, disability from sarcoidosis, and pulmonary function status. Lack of physician knowledge and poor physician communication were ranked of lowest concern. Concerns about ineffective medications and cost of medical care were also ranked relatively low. Patients overwhelmingly considered information from their doctor as very useful.
Conclusion: In this survey of over 1000 US sarcoidosis patients, their greatest concerns were fear of poor clinical outcomes. The patients were relatively less concerned about their doctors' knowledge about sarcoidosis and poor physician communication. Although patients expressed significant concerns about poor HRQoL, not all domains of HRQoL were equally affected. US sarcoidosis patients rank concerns about disease progression higher than disease impact on HRQoL.
Keywords: Fatigue; Health-related quality of life (HRQoL); Patient concerns; Patient perceptions; Patient priorities; Sarcoidosis; Shared decision-making (SDM); United States (US).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

