Residual pain and fatigue are affected by disease perception in rheumatoid arthritis in sustained clinical and ultrasound remission
- PMID: 39841373
- PMCID: PMC11865154
- DOI: 10.1007/s10067-025-07331-0
Residual pain and fatigue are affected by disease perception in rheumatoid arthritis in sustained clinical and ultrasound remission
Abstract
Objective: Regardless of remission status, residual pain (RP) might persist in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The aim of this study was to characterize RP, its perception, and patient-dependent features and to evaluate its possible association with residual synovitis in patients with RA in remission.
Methods: Ninety-seven patients with RA, including 68 in sustained clinical and ultrasound remission (Rem/RA) and 29 in high/moderate DAS28-CRP disease activity (H-Mo/RA) were enrolled in the study. Thirty patients with fibromyalgia were enrolled as a control group(FIBRO). At study entry, demographic, clinical, ultrasound characteristics, and pain dimension assessment (VAS-pain, FACIT, CSI, GHQ, and RAID) were collected for each patient. RA patients underwent synovial tissue biopsy to evaluate the degree of synovitis using the Krenn synovitis score (KSS).
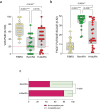
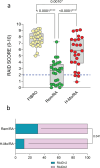
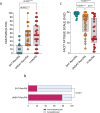
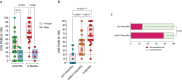
Results: Forty-eight percent of Rem/RA still declared unacceptable pain (VAS-Pain > 20) compared to 80% of H-Mo/RA patients (p < 0.0001). Furthermore, Rem/RA patients presented comparable levels of pain dimension assessment regardless of KSS. However, classifying Rem/RA group based on RAID score (< 2 as satisfied SAT-Rem/RA and ≥ 2 as unsatisfied UNSAT-Rem/RA), SAT-Rem/RA group presented a lower grade of VAS-Pain (p < 0.0001), lower percentage of patients with an unacceptable pain (p < 0.0001) and lower grade of fatigue(p < 0.0001) compared to the UNSAT-Rem/RA patients. The percentage of SAT-Rem/RA patients who presented a disease flare did not differ from UNSAT-Rem/RA over the 24 months of follow-up. Finally, female Rem/RA patients presented higher VAS-Pain compared to male Rem/RA (p = 0.0119).
Conclusions: Moreover,73% satisfied female Rem/Ra patients presented an acceptable pain compared to 23% unsatisfied female Rem/RA patients (p = 0.001). RP in RA patients in remission can represent the way by which the patients communicate their state of non-acceptance of the disease. It can be useful to treat RP with the appropriate treatments. Key Points • Rheumatoid arthritis patients still reported unacceptable residual pain despite sustained clinical and ultrasound remission and despite the low grade/absence of histological synovitis. • Only a small rate of rheumatoid arthritis patients in sustained clinical and ultrasound remission showed residual pain as part of a central sensitivity syndrome or psychiatric disorders. • Rheumatoid arthritis patients in sustained clinical and ultrasound remission complained residual pain and fatigue as part of not acceptance of disease and/or dissatisfaction in the disease management.
Keywords: Pain; Patient-reported outcomes; Remission; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standard. Disclosures: None.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

