Standardized pipelines support and facilitate integration of diverse datasets at the Rat Genome Database
- PMID: 39841812
- PMCID: PMC11753291
- DOI: 10.1093/database/baae132
Standardized pipelines support and facilitate integration of diverse datasets at the Rat Genome Database
Abstract
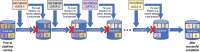
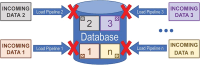
The Rat Genome Database (RGD) is a multispecies knowledgebase which integrates genetic, multiomic, phenotypic, and disease data across 10 mammalian species. To support cross-species, multiomics studies and to enhance and expand on data manually extracted from the biomedical literature by the RGD team of expert curators, RGD imports and integrates data from multiple sources. These include major databases and a substantial number of domain-specific resources, as well as direct submissions by individual researchers. The incorporation of these diverse datatypes is handled by a growing list of automated import, export, data processing, and quality control pipelines. This article outlines the development over time of a standardized infrastructure for automated RGD pipelines with a summary of key design decisions and a focus on lessons learned.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

